Let's talk about something downright stealthy and sinister known as Trojan horse malware.
Imagine receiving a seemingly harmless email or download. The moment you click on it, what seemed benign reveals itself for the mischievous intruder that it is. This 'Trojan Horse' then proceeds to secretly create an unauthorized entryway into your digital life, much like a burglar installing a hidden back entrance to your house.
Once inside, these hackers start scavenging through your personal data, targeting things like your personal details, banking passwords, and even your precious selfies! What's even more terrifying is that these cyber thieves can launch more attacks from within your system, like mercilessly encrypting your data and forcing you to pay up to get it back. This atrocious act is known as a ransomware attack.
The terrifying aftermath of a Trojan horse malware attack can range from loss of sensitive personal information to monetary damage, and even to nation-wide cyber-infrastructure disruption. Here are a few examples of what these illicit attackers can do:
These nefarious cyber activities underscore the importance of understanding and recognizing trojan horse malware. Next up, let's delve into some strategies to effectively defend against such attacks. Remember, knowledge is the first line of defense!
For instance, consider the pernicious types of malware like ransomware, adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, Trojan horse, spyware, browser hijacker, keyloggers, bots, botnets, RAM scraper malware, crypto-jacking, and more. Each type has unique characteristics and impacts computer systems in distinct ways. Understanding these specifics is our first line of defense.
Preventing malware attacks isn't just about understanding them, but also implicates on-going practical measures. Regular software updates can patch vulnerabilities that malware might exploit. Being savvy about potential threats such as suspicious emails or sketchy downloads is another crucial preventive step.
Malicious software or "malware" encompasses a broad spectrum of harmful computer programs used by hackers to illicitly access systems and data and cause damage to computers, servers, or networks. This definition applies to an array of malware such as viruses, worms, trojans, and other nefarious programs. This article focuses on the concept of Trojan horse malware, drawing parallels to the famous Greek myth. In this story, deceptive tactics influenced the course of events. In a similar vein, Trojan horse malware deceives victims, masquerading as legitimate software while masking a harmful program.
Imagine an innocent-looking email attachment appearing like a genuine software product. However, upon opening, this Trojan installs automatically on your device. A nefarious attacker has now gained unauthorized access to your system. This is the modern-day cyber equivalent of the wooden horse that once hid soldiers within its hollow belly.
It is crucial to be aware that Trojan horse malware is not the sole threat lurking in the digital sphere. Other forms of malware include ransomware, adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, spyware, browser hijackers, keyloggers, bots and botnets, RAM scraper malware, and crypto-jacking. While each operates differently, the common thread lies in their ability to invade, damage and compromise digital systems while staying under the radar. Let's take ransomware as an example. This type of malware locks your digital files and demands a "ransom" to release them. The unsuspecting user is left feeling powerless and may feel forced to comply with the hackers' demands.
These malware attacks can generate immense losses, such as business opportunities going down the drain, prolonged network and system downtime, irretrievable loss of critical data, and severe damage to reputation. The best defense incorporates preventive measures tailored to each type of malware. A good starting step might be ensuring all your software is up-to-date, as out-of-date software can have vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit.
In the fight against cyber threats like malware, information is power. Understanding the types of malware and their operational strategies is your first line of defense. Stay informed, stay vigilant.
However, spyware isn't the only threat; there are many other malware variants out there. For instance, we have adware, harmful software that bombards you with unwanted ads. Then there's the deadly ransomware that can lock you out of your system until you pay a ransom. Keyloggers secretly record your keystrokes to steal sensitive data, while Trojans masquerade as legitimate software. Not to mention the more complex malware such as bots and botnets, RAM scraping malware, or crypto-jacking that can bring your system to a standstill.
Moreover, it's critical to remember that these cyber threats can have severe consequences that reach far beyond mere annoyance. For example, falling prey to spyware can lead to stolen business secrets, opening the door to lost opportunities and potentially irrevocable damage to your reputation.
So, how can you protect yourself? The first step is to arm yourself with knowledge about these threats. Understanding how they work enables you to identify potential attacks and take preventative measures. Strong, frequently updated passwords, installing genuine antivirus software, and keeping your system up-to-date are just a few of the steps you can take.
While it's essential to understand these intricacies, it's equally crucial to render this information accessible. We aim to break down complex technical jargon into simple, understandable language. This way, everyone, tech-savvy or not, can grasp the concepts and protect themselves effectively.
To delve deeper into this topic, feel free to explore other reputable sources for a more comprehensive understanding and comparison.
These hostile programs, under the collective term "malware," encompass viruses, worms, trojans, and more nefarious software that hackers employ to gain unauthorized access to data and systems.
For instance, imagine a well-known organization suddenly finding their systems compromised, their confidential data breached and their operations halted. This could be due to a particularly potent strain of ransomware, a type of malware that locks up a system until a ransom is paid. Learn more about ransomware here.
As one navigates the world wide web, a potential pitfall to be aware of is the risk of adware - unwanted advertising software. While some adware programs play fair, operating solely as ad-supported software, others have more sinister objectives, often leading to disruptions in internet services and even paving the way for harmful activities. Adware proves its nuisance by blending into legitimate programs, persuading users on a click-based bait, and reaping revenue on every successful entrapment. In 2020, 1,841,164 people fell prey to such adware attacks.
However, the online danger zone expands beyond adware, encompassing other malware types such as ransomware and malvertising. Ransomware, like its name suggests, holds a user's computer or data hostage, demanding a ransom for release. Malvertising, on the other hand, exploits online advertising mediums to spread malware. Backdoor attacks offer unauthorized access to systems, giving the attacker free rein to exploit the compromised system. Each of these possess distinct threats and mechanisms they employ to infiltrate and compromise unsuspecting systems.
To protect oneself, users must learn to identify malware threats. A sudden barrage of pop-ups, an unusually slow system, or altered browser settings could all be indicators of malware intrusion. It's also essential to keep software and antivirus programs updated, use strong, unique passwords, and download from trusted sources. These simple practices can do wonders in fortifying your defenses against these malware attacks.
Real-life examples of notorious malware help illustrate the kind of damage they are capable of. Take Petya, a piece of ransomware that caused international havoc by encrypting hard drives and demanding Bitcoin payments for restoration. Or consider Adwind, a cross-platform malware, that gained infamy for its broad targets, ranging from industries to individual users.
In comparing these malware types, one might notice that while adware and malvertising largely focus on flooding the user with advertisements, ransomware and backdoor attacks pose serious threats to user privacy and security. Certain malware like adware might primarily irritate users, while others like ransomware create a full-blown digital crisis.
Malware, quite simply, is software designed to harm your system or data. This umbrella term includes issues from the somewhat benign adware to more serious forms like ransomware. In conclusion, it is crucial to remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding your digital security.
Regardless of whether the malicious software is created by a lone wolf hacker or a state-sponsored entity, the damage inflicted to systems—be it a personal computer, a server, or an entire network—can be substantial.
Let's delve deeper into the world of malware, understanding their impact and how they shape the cyberthreat landscape!
The malicious software type known as a browser hijacker malware gives cybercriminals the ability to forcibly redirect online users to alternate web pages, which are often malicious in nature. This form of malware operates by altering the settings of a user's web browser without their consent, effectively leading them to unwanted web locations.
The risks of falling victim to browser hijacker malware can be severe: users may inadvertently download harmful software or leak private information. To understand its impact further, consider it in relation to other types of malware discussed in this article. While all malware has a detrimental effect on systems and data, browser hijacker malware uniquely breaches user trust by manipulating their online navigation.
To protect yourself from such intrusion, regularly update your software and avoid clicking on suspicious links. Be proactive in understanding the different malware types, as this knowledge is your first line of defense against cyber threats. Remember, the internet can be a minefield of potential threats, but with the right knowledge, you can navigate it safely.
One notorious example that demonstrates the severity of malware attacks is the infamous WannaCry ransomware incident, which targeted countless victims worldwide and caused significant operational disruptions and financial losses.
Various techniques are deployed by these cyber adversaries to execute malware attacks. The most common among these methods is through deceptive emails, a tactic that is as ubiquitous as it is damaging.
Now, let’s clarify what ‘unauthorized access’ means. In simple terms, it refers to when an entity gains access to a network, system, or data without being granted the necessary permissions. Imagine a stranger entering your house without your knowledge or consent; that’s how malware sneaks into a computer system.
Importantly, it’s not all doom and gloom. There are various preventive measures we can take to safeguard against such attacks. Regularly updating software, installing reputable security programs, practicing caution when opening emails from unknown sources, and refraining from clicking on suspicious links can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to malware.
In the realm of cybersecurity, the potential threats posed by various types of malware must not be overlooked. While there are many types of malware, this discussion focuses primarily on worms and viruses.
A worm is unique in its ability to replicate autonomously, causing potential disruption to network activities and IT infrastructure due to increased bandwidth consumption. Yet, it's important to mention that they might not necessarily inflict direct damage.
On the other hand, a virus moves around by embedding itself into documents and files, multiplying its potential of causing harm by altering the operations of a computer once activated. It is critical to note that unlike worms, viruses require some intervention from users, such as initiating a download or opening a file, to set off their malicious deeds.
However, the cybersecurity landscape is far broader, encompassing other malware types like ransomware, adware, and malvertising. Each of these possesses unique capabilities and potential impacts, necessitating a full understanding for comprehensive protection.
Prevention is invariably considered the best course of action. This includes maintaining updated software, using robust firewalls and antivirus programs, and cultivating responsible web browsing habits. Furthermore, understanding the potential impacts of each type of attack aids in fostering a proactive rather than reactive cybersecurity strategy.
In summary, while our attention here has been steered primarily towards worms and viruses, it's crucial to understand and protect against other malware threats. Educating oneself about these threats is the first step towards maintaining a secure digital environment.
Worms are standalone malware programs designed to infiltrate your computer or network, clone themselves, and silently infect other connected devices. They capitalize on security gaps and weak spots in your network, spreading their harmful code to all available devices.
The impact of these malware infiltrations can be devastating. They can undermine business transactions, cause extensive downtime to networks and systems, and result in the loss of critical information. Perhaps more damagingly, they can even tarnish reputations over the long term.
So, how to keep these threats at bay? Prevention is the key. It's imperative to undertake regular system updates, deploy reliable antivirus and antispyware software, and adopt safe browsing habits. Furthermore, knowledge about these threats is the best defense – if you recognize dangerous attacks and bolsters your defenses accordingly.
In conclusion, understanding malware is not just for tech whizzes – it’s something that anyone using a computer or device should be aware of. From worms to ransomware, being familiar with these threats and knowing how to protect yourself can keep your digital life secure.
Malware, also known as malicious software, is a type of harmful program used by hackers to exploit and gain unauthorized access to various technologies. It comes in different forms, such as viruses, worms, and trojans. Learn more about malware.Expanding from this, there are other related terms like adware and malvertising. Adware is a form of software that supports advertising and may sometimes be a gateway for hackers. On the other hand, malvertising refers to the use of online advertising to spread malware.Another potential threat is ransomware, a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system until a sum of money is paid. And crypto-jacking, which involves unauthorized use of someone's computer for mining cryptocurrency.These threats could manifest in various ways, such as the unwarranted addition of numerous toolbars to your web browser, unexpected slow loading of web pages, or even a sudden change in your default search engine.The impacts of malware attacks can be far-reaching within our digitally reliant society. Notably causing system downtime, leading to loss of crucial information, and potentially causing significant damage to business reputations.To protect yourself against these cyber threats, it's important to implement preventive measures such as regular system updates, the use of trustworthy anti-virus software, and gaining knowledge on how to identify and avoid suspicious emails or websites. To understand the severity of these issues, we can consider past incidents. [Insert malware-related incidents and their effects].Engaging in safe online practices can help prevent such occurrences, but remember, remaining vigilant and informed is your first line of defense.
Rootkits play a significant role in various forms of malware attacks. For instance, let's examine ransomware and backdoor attacks. Intruders manipulate rootkits to increase the potency of these attacks by hiding malicious activities in the system they've breached. Because of the stealth character of the rootkit, the compromised system or network might continue to function seemingly undisturbed – all while being under the control of the intruder.
Now, imagine the impact of a rootkit attack on a business. Any unauthorized access to business systems and data could lead to catastrophic commercial impacts like lost business opportunities, prolonged system and network downtime, and severe damage to the company's reputation. That’s why rootkits, though often unnoticed, are a sinister threat that organizations must be vigilant against.
So, how can we guard against rootkits? Precautions specific to rootkits include regularly updating and patching all software, employing robust security software that can detect rootkit behavior, and practicing safe browsing habits. Keep an eye out for common signs of a rootkit attack, like system slowdowns, unusual behavior of applications, and unexpected Windows reboots. Remember, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.
The risk of rootkits is real and severe. It's crucial that we all understand this threat, know how to spot it, and are equipped to guard against it. Endeavor to keep your cyber environment safe, and you'll contribute to the larger fight against this invisible enemy.
A keylogger malware program has the potential to pose significant threats, not through the direct damaging of systems, but by facilitating unauthorized access to highly sensitive data. These programs operate by storing the data they collect and transmitting it to malicious cyber criminals stationed elsewhere.
To illustrate, imagine a bank employee unknowingly downloading the keylogger malware by opening a phishing email. The malware then records every keystroke the employee makes - including login credentials for the bank's central system, private client data, and other critical information. The cybercriminals receive this information and can now potentially commit fraud, causing financial losses and reputational damage to the bank.
However, it's essential to not mistake a keylogger's lack of direct destruction with inoffensiveness. This notion that the malware "doesn't harm systems but instead grants unauthorized access to confidential data" is misleading. Unauthorized access alone can trigger severe repercussions across numerous levels. To be more precise, while keyloggers may not encrypt or delete data, they facilitate unpredictable security breaches which in themselves are highly detrimental.
Cybercriminals deplore keyloggers towards their ill-intentioned goal of extracting personal and financial information. They strategically place their malware to gather swathes of sensitive data, which they then exploit for unlawful monetary gains.
To protect against these threats, we recommend regular updates of security software, avoiding downloads from unfamiliar sources, and staying vigilant when opening emails from unknown senders. By fostering good cybersecurity habits, one can greatly reduce the risk of falling prey to keyloggers.
These RAM scrapers have advanced methods to trasmit the information they gather. They can inconspicuously store the read information locally or, more daringly, send it remotely to the individual or organization that instigated the attack.
Crypto-jacking malware, a malicious program that exploits JavaScript in a web user’s browser, serves the sole purpose of mining digital currency without the end-user's consent or knowledge. In a sense, it means the cybercriminal absconds the user's memory, CPU time, power consumption, and essentially their resources to achieve their own nefarious goals. But how does this form of malware exactly work?
The process of Crypto-jacking begins when the hacker infects a website or ad with a piece of code. When the unsuspecting user visits this infected site or clicks on the ad, the code starts operating, hijacking their computer resources for the hacker's own benefit. This type of unauthorized use of computer resources is sophisticated and usually goes unnoticed by users.
The consequences of Crypto-jacking can be dire, most notably a drastic reduction in device performance, high electric bills, and increased wear and tear on the computer system. Beyond the individual, businesses and organizations can find themselves facing financial loss and damage to their reputation should they become victims.
But, the question arises - how does crypto-jacking differ from other malwares? While other malwares may have destructive intent - such as corrupting files or stealing data - crypto-jacking has a more specific goal: the illicit mining of digital currency. Because of this specialized objective, crypto-jacking is often discretely carried out, quietly siphoning resources rather than causing ostensible harm.
However, you can protect yourself against Crypto-jacking. Maintaining up-to-date anti-virus software, installing ad-blockers, being cautious with suspicious emails and links, and regularly monitoring your computer’s performance can safeguard against these intrusive attacks.
Still thinking this is just a theoretical issue? Think again. Real-world instances of Crypto-jacking have impacted organizations worldwide, including British Airways and Ticketmaster, which incurred significant costs due to undetected crypto-jacking activities.
Understanding the dynamics of the Crypto-jacking malware is essential to ensure the safety of your digital life, which has become an integral part of our lives in this digital era.
To better understand cybercriminals' tactics, let's delve into the kinds of malware attacks. Using social engineering, cybercriminals may lure their targets into various ambushes, including ransomware, adware, and botnets, among others. For instance, think about how an unsuspecting user could be tricked into installing what seems to be a legitimate app, only to find out later that it was ransomware. Another scenario could involve cybercriminals using social engineering to exploit their victim's device for crypto-jacking. Real-life illustrations of these attack scenarios can clarify how dangerous these threats can be.
Apart from these, there are harmful payloads that these malware carry, for instance, the siphoning of sensitive data from an infected computer. Tying this back to the broader consequences, it isn't just about the immediate loss of data. It could lead to loss of business opportunities, or worse, damage the company's reputation. Thus, understanding these tactics gives us a glimpse of how critical network and data security are in our digital age.
Cyberthreat actors, or more commonly known as "Cyber adversaries", exploit various techniques to launch malware attacks, these being malicious software activities aimed at unauthorized intrusion into secure data and violation of protected systems and networks. The arsenal of malware attacks is diverse and includes various types such as viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
One of the preferred methods adopted by these cyberthreat actors for delivering malware is via email. To provide a real-life instance, a fraudulent email might portray as a trustworthy entity, tricking recipients into opening an infected file, or directing them to a compromised website, thus facilitating the contamination of the target system or network.
A staggering statistic shows that 94% of reported malware attacks begin with a single email. It's worth noting that this statistic broadly encompasses global incidents and is not limited to a specific industry or timeframe.
Understanding these attacks' intricacies can be daunting, but knowing how to shield oneself is a feasible task. Always scrutinize emails for legitimacy before interacting with their content, keep applications up-to-date with the latest security patches, and maintain a robust antivirus protection system can drastically lower the risk of falling victim to these cyber adversaries.
In essence, cyber adversaries employ a variety of malware attack techniques with email being a common delivery method, contributing to a vast majority of these attacks. However, with vigilance and implementing best cybersecurity practices, one can mount a formidable defense against these threats.
A deep dive into malware attributes and traits can help safeguard against these digital threats. A proactive approach to protection can serve as the ideal defense. To this aim, we must also be mindful of our language usage, without dwelling on repetitive phrases such as "malware attacks". A richer vocabulary will provide a better reading experience.
In conclusion, understanding the makeup of malware attacks is a crucial first step. But equally important is staying current on the latest strains, fully grasping the impact they can have and strategically bolstering your defenses to stave off these threats. Being informed and prepared can give you the edge in this ongoing battle against digital threats.
Apart from these, there are harmful payloads that these malware carry, for instance, the siphoning of sensitive data from an infected computer. Tying this back to the broader consequences, it isn’t just about the immediate loss of data. It could lead to loss of business opportunities, or worse, damage the company’s reputation. Thus, understanding these tactics gives us a glimpse of how critical network and data security are in our digital age.
In the realm of cyber threats, one term tends to stand out - Malware, or malicious software, refers to a set of harmful computer programs that hackers resort to for unauthorized access to systems and data. Viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware are all types of malware that cause damages to computers, servers, or networks. An emerging threat in this sphere is the advent of hybrid malware attacks.Hybrid malware ingeniously combines different malware forms, borrowing their characteristics and functionalities to perform multiple attacks simultaneously. For instance, a hybrid malware having features of a worm and a virus can manipulate legitimate program codes like a virus while using the worm's capabilities to spread across a network and hide in a computer’s memory. In addition to these, other less-discussed, albeit significant malware attacks include adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, Trojan horse, spyware, browser hijacker, keyloggers, bots and botnets, RAM scraper malware, and crypto-jacking. Each carries unique risk features and credibly adds to the overall complexity threat landscape.The damage inflicted by these malware programs, especially by hybrid malware, is significant and devastating. Potential fallouts include opportunities for performing business operations lost, network and system downtimes, loss of critical information, and damaged reputation. As such, understanding the threat posed by these malware forms is of utmost importance.One can deploy effective preventative measures, like regularly updating software and firewalls, adopting safe browsing habits, or using authentic anti-malware tools, to protect against such attacks. Remember, understanding and awareness is the key to cybersecurity hygiene.This type of malware uses scare tactics such as displaying fake alerts for non-existent malware attacks on your computer. Ignoring these can lead to more serious cyber threats, which is why they typically prompt immediate action. This prompt often comes with a recommendation to download a specific software tool, often positioned as a solution but in reality, it’s malware that could lead to unauthorized system access, data breaches, and even financial loss.Given the potential severity of these outcomes, it's crucial to know how to protect yourself. The first line of defense is staying informed about the common types of scareware and their tactics. It’s equally important to maintain a robust cybersecurity suite, including trusted anti-malware and anti-spyware tools. Be sure to keep these programs updated to ensure maximum protection against ever-evolving scareware strategies.What does this injected code do? It is engineered to install malevolent software automatically onto anyone unfortunate enough to stumble upon the compromised site. No interaction is required; merely entering the site triggers the installation. Hence, the label 'drive-by' encapsulates the essence of this attack type - it happens fast and needs no interaction from the victim.Beyond the installation, the harmful scripts also have another dastardly function - redirecting the unaware user to a website riddled with more malware. Imagine it like being swept away by a rip current towards a shark-infested water.For a clearer picture, consider this scenario - suppose the malicious code is a devious web shell script. As soon as you click on the compromised website, it silently installs malware on your computer, which can then "phone home" to the hacker's server, giving them unauthorized access to your system. That's how sneaky and intrusive these scripts can be!Now that you understand what's happening behind the scenes in a drive-by attack, let's discuss the preventative measures. Being aware, vigilant, and proactive can help protect you from falling prey to such attacks. Ensuring your software is updated, using a trusted firewall and antivirus, practicing healthy browsing habits, and refraining from clicking on links or websites that seem suspicious are some of the steps you can take.Besides general malware, different types of specific malware such as Trojans, ransomware, and spyware, can also be delivered through drive-by attack practices. Each type brings its own set of tools and techniques into the mix making the realm of drive-by attacks complex and multi-faceted.Let's break it down: WMI is a set of tools and extensions provided by Windows that allows scripted languages to manage Microsoft products, while PowerShell is a powerful scripting language geared towards task automation and configuration management.Fileless malware cleverly uses these platforms to inject damaging codes. Their popularity among cybercriminals is due to the fact these are reliable and trusted apps, crucial for executing system-oriented tasks seamlessly. These features make them ideal targets for fileless malware attacks. Tragically, these kind of attacks were reported to have skyrocketed by a staggering 900% in 2020, as stated in this study.But, why did fileless malware attacks increase so much in 2020? There could be several contributing factors like increased digital transformation of businesses, higher dependence on digital platforms due to remote work, to name a few. It's of paramount importance to secure your system against such threats.While the focus here is on fileless malware, let's not forget about other forms of malware such as viruses, worms, trojans, etc. They might not be as sophisticated as fileless malware, but their potential to cause significant damage is world-recognized.It’s inherently important to remind everyone of the potential consequences resulting from these harmful attacks. They can lead to personal data theft, financial loss, and in worst cases, can leave your system utterly non-functioning.Nevertheless, every problem has a solution. Safeguarding against these attacks involves installing and regularly updating a robust anti-virus program, activating firewalls, keeping software updated, and using two factor authentication wherever possible.. Described simply, malware is a form of malicious software. Its nature and effects can range from disruptive to devastating, whether it manifests as viruses, worms, trojans, or other harmful programs. Cybercriminals use malware as a tool to gain unauthorized access to systems and exploit data.
It's critical to note that businesses represent the primary target for most malware attacks. One might wonder why businesses? The answer is straightforward - businesses often have more valuable data and, surprisingly, less secure systems than might be expected. This element of risk and susceptibility tremendously increases when businesses are involved.
What's even more unsettling is that malware doesn't come singularly; it exists in families. Currently, four major families are seeding chaos in the world of Point of Sale (POS) systems. These groups (the top four malware families) have been identified as the leading culprits behind the majority of malware-related issues in POS systems. Their activity ranges from data breaches to financial loss.
This article intends to shed light on 'RAM scraper malware,' one of the primary suspects within these families. As we further delve into the topic, we'll focus on this particular type of malware, its characteristics, and preventive measures that can be taken.
Essentially, a RAM scraper works by scouring the layers of a computer's RAM seeking unprotected sensitive data. This focus on volatile memory allows the malware to capture information that might otherwise be secure. Instances of its use in major attacks have highlighted the threat it poses to both individuals and corporations.
The repercussions of a RAM scraper attack can be quite severe. Businesses stand to lose potential opportunities due to compromised sensitive data, experience significant downtime in their network or system, and potentially suffer damage to their reputation.
Understanding these attacks is a powerful first step towards preventing them. A myriad of preventative measures and best practices exist that can protect one from falling victim to these attacks. These include robust cybersecurity programs along with user awareness and vigilance.
RAM scraper malware serves as a sobering reminder of the constant evolution of cyberthreats. It's crucial for all internet users to stay informed, vigilant, and maintain good cybersecurity practices to protect themselves.
Malware, an intrusive software, manifests in multiple forms and spyware is one such dangerous variant that severely compromises user privacy.
Spyware, as the name implies, monitors user activities and possesses the potential to install additional software, and even tamper with the system's security settings. Yet, these actions barely scratch the surface of the spyware capabilities. To grasp their true potency, it's crucial to delve deeper into how they operate, investigate the severity of threats they pose, and study real-world incidents where spyware attacks have led to significant damage.
You're encouraged to explore the comprehensive section dedicated to spyware within this article. Here, you'll find exhaustive details on the detrimental effects of spyware and guide you on how best to protect your system against them.
Now, let's simplify this menace to layman's terms: Consider spyware as 'stealthy observers' - they silently track your online habits. While that might not sound harmful, remember that they may silently install additional malicious software and manipulate your device's security settings.
But there's no need to panic! There are robust measures to guard against this threat. Implementing antivirus software and diligently updating your system could significantly help ward off spyware. Yet, this is just the tip of the iceberg in terms of counter-strategies. The article also covers a variety of tools and practical advice to help individuals and organizations combat malware effectively.
Beyond just detailing the perils of malware, this article is aimed at equipping you with knowledge and tools to protect your digital milieu. We hope this balanced content approach aids in creating an informed and vigilant online community.
Preventing malware attacks isn’t just about understanding them, but also implicates on-going practical measures. Regular software updates can patch vulnerabilities that malware might exploit. Being savvy about potential threats such as suspicious emails or sketchy downloads is another crucial preventive step.
Scareware malware, a specific type of malicious software, employs manipulation techniques to trick internet users into downloading or purchasing harmful programs that they do not need. These tactics take advantage of the user's innate anxiety, belief in potential dangers, or shock. But what does that actually mean? Take, for instance, a scenario where you receive a seemingly legitimate but false alert on your computer-screen suggesting that your PC has been infected with a dangerous virus. In a state of panic and believing the fabricated threat to be real, you might be compelled to follow the given directions and inadvertently download the harmful scareware software.
Delving deeper into the destructive capabilities of such programs, beyond the deceit and manipulation, they can cause significant harm to your computer systems, ranging from disrupting your machine's operation to extracting sensitive information. Comprehending the implications of these attacks helps underline the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
According to cybersecurity reports, scareware attacks are far from rare. Their prevalence across the globe and the financial impact they cause are notable topics worthy of discussion. It is a favored tactic among cybercriminals, contrasting with other types of malware which might be more challenging to execute. A comparative overview of scareware alongside other malware varieties can provide a clearer perspective of the cyber threat landscape.
The danger from fileless malware stems from its stealthy approach and the potential impact it can have. When these stealth attacks breach your systems, they can cause real-world fallout - businesses can lose valuable opportunities, and significant network downtime can occur.
So, how can you safeguard against these threats? Start with high-quality, continuously upgraded security software. Couple this with secure online activities and an eye for recognizing suspicious behavior online. Awareness and proactive security measures are your best defenses.
Understanding malware, and fileless malware in particular, doesn't have to be confusing. In simple terms, fileless malware is a type of cyberattack that uses your own safe, trusted software against you. Not only is this an intriguing concept, but it's also a vital one to grasp in our increasingly digital age.
To delve deeper into this topic, feel free to explore other reputable sources for a more comprehensive understanding and comparison.
Let’s take a look at the most prominent malware exploits today.
These hostile programs, under the collective term “malware,” encompass viruses, worms, trojans, and more nefarious software that hackers employ to gain unauthorized access to data and systems.
For instance, imagine a well-known organization suddenly finding their systems compromised, their confidential data breached and their operations halted. This could be due to a particularly potent strain of ransomware, a type of malware that locks up a system until a ransom is paid. Learn more about ransomware here.
Another prevalent malware is adware. Imagine surfing the internet and your screen gets flooded with unwanted, distracting ads. This is the work of adware, a software that displays unwanted ads and can pose potential risks to your system and privacy. Read more about adware here.
Regardless of whether the malicious software is created by a lone wolf hacker or a state-sponsored entity, the damage inflicted to systems—be it a personal computer, a server, or an entire network—can be substantial.
Let’s delve deeper into the world of malware, understanding their impact and how they shape the cyberthreat landscape!
1. Understanding Ransomware Attacks
A Comprehensive Overview
Ransomware attacks constitute a significant aspect of cyber threats in today's world. As a form of malicious software, ransomware holds data at ransom by locking it and requiring payment to unlock it. By having a clear understanding of how this malicious software operates, its deployment methods, and the possible damage it can cause, one can better appreciate the weight of its threat.
What Ransomware Does
Encryption is the main weapon utilized in ransomware attacks, locking the data and making it inaccessible. Various methods are used to deliver this harmful software that range from email attachments to infected software apps. Once installed, the damage caused can be severe, potentially leading to data loss or financial havoc.
Staying Safe From Ransomware Attacks
The knowledge of protecting one's systems from these attacks is crucial. Implementing strong security measures, constantly backing up important data, and avoiding suspicious emails or websites helps guard against this type of malware attack.
Illustrative Scenarios
To gain a clearer picture of the scale and severity of ransomware threats, consider the real-life instances of ransomware attacks that have crippled businesses and organizations worldwide.
Simplifying Complexity
While delving into ransomware attacks can involve complex technicalities, the effort is made here to simplify and balance these aspects. THIS aims to equip the reader with essential knowledge while avoiding jargon or overly technical language that could be off-putting.
Providing Clarity
In conclusion, understanding ransomware attacks can appear daunting. However, with clear and concise language and the effort to break down complex areas, it is hoped that this content educates and prepares the reader to navigate the digital sphere safely. Remember, the focus is on aiding comprehension, not creating confusion.

Ransomware is a type of malicious software, or malware, which can encrypt vital data and prevent users' access to their computer systems. Notably, cybercriminals utilize ransomware attacks to extort victims into offering a certain financial sum in order to obtain the decryption code. Generally, these malevolent actors demand the ransom in hard-to-trace cryptocurrencies. Delay or failure in payment can lead to drastic consequences such as permanent deletion or unauthorized sale of sensitive information on the hidden networks of the dark web.
Besides ransomware, there exists a myriad of other malware attacks which pose a significant cyber threat. Distinguished by their unique attributes and impacts, each malware type warrants its own comprehensive overview.
Phishing emails and deceptive websites serve as common ransomware delivery channels. They cleverly urge users to click on disguised harmful links or download malicious files, thus inadvertently inviting the ransomware into their systems.
Ransom demands through cryptocurrencies offer the culprits an added advantage, as they are difficult to track and provide a veneer of anonymity to the perpetrators. The possibility of the sensitive data being deleted, leaked, or sold is usually the coercive strategy employed by these criminals to compel victims to pay the demanded ransom swiftly.
However, implementing proactive measures such as utilizing up-to-date security software, carrying out regular data backups, and staying vigilant regarding suspicious links and emails, can significantly reduce the risk of falling prey to these nefarious malware attacks.
Click here for a comprehensive understanding of ransomware and how you can safeguard your digital presence from such attacks.
Security breaches constitute a daunting challenge for businesses today, with one form of attack standing out prominently: the ransomware. Ransomware infiltrations, along with other malicious threats such as adware and spyware, have been wreaking considerable havoc, especially impacting businesses. The aftermath that these attacks leave behind are often disastrous, costing businesses not only their finances but also their reputation.
The danger of these particular kinds of malware attacks is worryingly common. According to a recent study, an alarming number of over 304 million ransomware attacks were reported globally in 2020. It's not just the frequency that's alarming, but also the financial implications. On average, a single ransomware attack could set a business back by as much as $133,000. Even more disturbing, this type of threat seems to be on the rise, with analysts predicting that 2021 will see a ransomware attack on businesses every 11 seconds, resulting in an estimated recovery cost surpassing $20 billion.
Why are ransomware attacks gaining such traction amongst cybercriminals? Their effectiveness lies in their ability to deny access to critical business information and systems, thereby effectively halting operations until a ransom is paid. This type of attack, in comparison with other forms of malware, strikes at the heart of a business's operability, hence the substantial financial demand in return for reinstating access.
As alarming as this might sound, all is not lost. Companies can adopt preventive measures to guard against such attacks. Incorporating robust security protocols and comprehensive data backup systems can drastically reduce the risk - a small investment now could save your business a fortune later. Stay informed, vigilant, and proactive in the face of this evolving threat landscape.
2. A Look into Malware Attacks: The Virus Threat
Our world is becoming increasingly digital, and with that comes increased vulnerability to cyberattacks, notably those of the viral kind. Here, we'll delve into the landscape of malware attacks, emphasizing the significant role viruses play. We'll light our path with real-world examples and case studies of some of the most notable viral invasions.
We'll illustrate the actual damage these cyber pests can invoke, using compelling narratives of personal and organizational recovery, giving you a true testament to the power and resilience inherent in the human spirit. It's a macabre picture we paint - but a crucial one for understanding fully to pave the wave for digital safety.
We'll take the virus apart, exploring its lifecycle, from its initial penetration of your security measures into its spread, inflicting damage upon your personal or professional systems. A true understanding of these threats offers the first step to countering them.
Finally, we will equip you with the tools to guard against malware attacks, including preventative measures, ensuring you are ready to face any cyber threat head-on. An informed public remains the best defense against cyber pitfalls, and we're committed to keeping you, our reader, informed and safe.

Malware, or malicious software, comprises of multiple types of harmful entities that threaten your computer system. Taking several forms, including viruses, ransomware, and adware, each kind of malware operates distinctively, causing unique types of damage.
Ransomware
Adware
Real World Incidences
WannaCry ransomware attack
Preventive Measures
Cybercriminals are continuously looking for ways to disrupt our digital world by creating computer viruses for a variety of reasons. Some aim to sabotage a network leading to the denial of critical services to an organization. Others are motivated by the prospect of monetary gains, while some simply use it as a means to demonstrate that even a highly secured IT environment is not immune to attacks.
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the sophistication of these attacks. Some cybercriminals are leveraging newer technologies to develop and execute more advanced computer virus attacks. It is crucial to mention specific types of these advanced malware attacks; including ransomware, adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, and the infamous trojan horse.
Staggeringly, at least 6,000 new viruses come into existence every month! Considering the growing number of these virtual threats, let's examine the direct impact of these cybersecurity breaches on businesses, personal accounts and the specific types of malware attacks mentioned earlier.
The constant influx of new viruses underlines the urgent need for robust preventative measures. As we delve deeper into this digital era, only our preparedness and knowledge can shield us from the ever-evolving cyber threats. Detailed understanding of these threats not only adds to our knowledge but also highlights the importance of security in the cyber realm.
3. A Deep Dive into Adware Attacks
In this section, we will examine Adware Attacks in detail. We will start with a simple explanation of what Adware is and how it primarily infiltrates into our systems. Several examples of past Adware attacks and the consequences will provide a clear understanding of its severity.
We will also explore potential indicators of an ongoing Adware attack, shedding light on the common distribution methods used by such Adware. This knowledge is crucial in recognizing whether your system is under threat.
But fear not, we do not just stop at identifying threats. It is equally essential to know how we can fend off these attacks or remove any existing Adware from our systems. Therefore, we will outline useful tips on protecting your systems from Adware Attacks.
Lastly, we will identify any relevant software or updates that can help you guard against Adware threats, giving you all the tools you need to combat these attacks effectively. By the time you've finished this section, you will have a comprehensive understanding of Adware Attacks and how to protect yourself against them.

The prevalence of malware attacks, a rising threat in our increasingly digital world, cannot be overstated. In a shocking statistic, 94% of malware strikes originate from seemingly innocent emails.
Malign software, or malware, refers to a broad umbrella of malicious programs used by cyber attackers to breach secure networks and access sensitive data without authorization.
One notorious example that demonstrates the severity of malware attacks is the infamous WannaCry ransomware incident, which targeted countless victims worldwide and caused significant operational disruptions and financial losses.
Various techniques are deployed by these cyber adversaries to execute malware attacks. The most common among these methods is through deceptive emails, a tactic that is as ubiquitous as it is damaging.
Now, let's clarify what 'unauthorized access' means. In simple terms, it refers to when an entity gains access to a network, system, or data without being granted the necessary permissions. Imagine a stranger entering your house without your knowledge or consent; that's how malware sneaks into a computer system.
Importantly, it’s not all doom and gloom. There are various preventive measures we can take to safeguard against such attacks. Regularly updating software, installing reputable security programs, practicing caution when opening emails from unknown sources, and refraining from clicking on suspicious links can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to malware.
While discussing these malicious attacks, it's important to understand that there are different types of malware, each with its unique behavior and potential damage. These include viruses, worms, trojans, and more. Future sections will delve into more specifics of each type and their corresponding preventive measures.
Despite their insistent ad projection, adware programs are usually seen as benign by nature as most are primarily focused on advertisement dissemination rather than causing explicit harm to the system. However, this doesn't render them any less a form of malware. In the cybersecurity space, the intention behind their creation, and the nuisance associated to unsolicited ad serving, are prevalent factors contributing to their classification as a form of malware. This is where things get interesting; we start seeing connections and overlaps between Adware and other forms of Malware, like ransomware, spyware, or even trojans.
Like other forms of malware, adware also poses potential privacy concerns due to imbalance in advertisement practices. If not handled effectively, the deployment of such ads could infringe upon the user's privacy rights. Therefore, understanding the adware attacks - how they happen, specific examples, their effects, both personal and at an organizational level, and most importantly, how to protect yourself from these attacks - is pivotal for all internet users. It's also worth highlighting the practical defense measures you can adopt against adware attacks so that you can steer clear of these stealthy, nagging intrusions and ensure a safe browsing experience.
Based on their nature, adware attacks can be highly annoying since they pop up at any time when a user is accessing internet services. Adware attacks typically distinguish themselves as legitimate programs or piggyback on other running programs to trick users into clicking and installing them. Adware attacks remain to be highly profitable since they generate revenue automatically once a user clicks them. In 2020, some 1,841,164 people were victims of adware attacks.
4. Malvertising
Experiencing a warning about low memory on your device due to a malware attack is all too common for internet users. It's often accompanied by a prompt to 'clean your computer using antivirus tools'. But clicking that oh-so-tempting banner usually downloads more malware or reroutes you to a website swarming with these malicious programs.
In essence, these deceptive tactics mirror a type of malware threat called adware. However, adware is not the only malware type that plagues the internet realm. There are others, such as ransomware that locks users out of their systems until a ransom is paid or backdoor attacks and trojan horses that grant cybercriminals unauthorized access to systems.
Case in point? The infamous WannaCry ransomware attack that wreaked havoc on countless computers globally. The rampant proliferation of such threats underlines the necessity to safeguard your device vigorously.
Thus, being proactive is crucial. Exploring reliable anti-virus software, staying clear of suspicious emails or websites, and keeping your digital devices updated are just a few preventive measures you can adopt to shield your systems against these cyber threats. Remember, awareness and prevention can make a world of difference in the panorama of cybersecurity.
Malicious advertising, widely known as 'malvertising', is a deceptive technique employed by cyber attackers. They infuse harmful malware into digital advertisements on various pubs and ad platforms. With these camouflaged adverts, hackers catch users off guard, deceiving them to click and subsequently distribute malware.
Let's look at some instances. In certain scenarios, these advertisements appear legitimate to unsuspecting users, luring them into clicking. Well-known brands are often mimicked in these faux advertisements. Quite often, successful attacks update the malicious code within the user's computer, gaining unlawful access to their systems and data, while other attempts get spotted and dismissed before causing any damage.
Malvertising is but one of the many types of malware cyber attacks. Others permeate the digital sphere, including ransomware, adware, botnets, each with their unique motives and modus operandi. However, the common denominator is their use of malicious software to cause harm to computers, servers, or networks. In context, 'malvertising' is a specialized type of adware.
Over and beyond the spreading of malware, malvertising disrupts more than what meets the eye. It serves as a conduit to violate user's online security and privacy, lead to financial losses, cause data breaches, and even compromise a corporation's reputation.
Prevention is always the best cure, and this adage is fitting in defending against malvertising attacks. Simple practices like regular software updates, installing reputable ad-blockers and exercising cautious online behavior go a long way.
Remember, the ultimate goal of cyber attackers through malvertising is to inject malware - a dangerous software designed to disrupt and gain unlawful access to your system. Stay vigilant and help create a safer online ecosystem for all.
Throughout 2020's second quarter, the threat of 'malvertising' - a malicious form of online advertising designed to spread malware - soared to 72% above the usual average. This worrying increase can be attributed to cyber criminals seizing opportunities presented by the global COVID-19 pandemic. It's important to note, however, that malvertising is just one form of malware attack. This piece also delves into other manifestations of the threat, demonstrating the extensive field of exploitative techniques that malicious actors exploit.
So what can be done to guard against these pernicious attacks? It's a complex issue, but we discuss preventive measures that can be enacted in the article, offering readers an understanding of how best to secure their digital lives.
Perhaps you're wondering how the pandemic has contributed to this surge in malvertising threats? As uncertainty grew, so too did the opportunities for cyber criminals to exploit the fears and vulnerabilities of their targets. We delve deeper into this topic, offering insights into the specific tactics employed during this unprecedented time.
Understanding Browser Hijackers: A Comprehensive Analysis.
When we talk about malware attacks, the term "Browser Hijacker" often raises concern. In order to demystify this topic, let's delve into what a Browser Hijacker exactly is, its modus operandi, and the potential risks linked to it. We'll also discuss how a system might get infected and provide ways to spot the presence of a Browser Hijacker. Finally, we'll guide you on preventive measures you can take or steps to purge the malware in case your system is already compromised. It is our aim to present this information in a straightforward, jargon-free manner so that no matter what your computer literacy level is, you will find it easy to follow.

A backdoor attack represents a stealthy method that expertly sidesteps established encryption and verification protocols present in a digital product, network, computer, or embedded device.
Imagine, for instance, a scenario where a seemingly innocuous software update infiltrates your computer system, bypassing the usual safety features. Unbeknownst to you, this ‘update’ is a backdoor attack in disguise, surreptitiously gaining access and embedding itself into your system. This real-world example showcases a typical execution of a backdoor attack, giving you a clearer understanding of its covert nature.
One might wonder, what are the potential repercussions of such an attack? The impacts can be severe and far-reaching. They can cause a halt to network operations or worse, lead to the loss of critical, confidential information. This happens as the backdoor attack capitalizes on the privileged stealth access it has obtained, allowing it to manipulate or extract data, resulting in these dire outcomes.
Now that you're aware of the gravity and subtlety of a backdoor attack and its implications, let’s dive into practical mitigation measures you can employ. In our software update example, verify the source and authenticity of the software provider before allowing any updates. Regularly update your network security protocols to detect and defend against such stealthy attacks. By quickly understanding the mechanisms and potential fallout of a backdoor attack, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your digital assets.
A backdoor attack, a critical category within the larger umbrella of malware attacks, is perpetrated by threat actors who stealthily embed a malicious program like a trojan horse in a secluded component of a running software, or they may use a separate harmful program masquerading as legitimate software.
To delineate, a backdoor attack is a sophisticated malware offensive where assailants clandestinely infiltrate a system bypassing standard authentication procedures. Though all forms of malware attacks wreak havoc on an organization's or individual's digital infrastructure, backdoor attacks have their unique attributes. Unlike ransomware or adware which tend to be more flamboyant, backdoor attacks prefer staying under the radar with the intent of securing long-term unauthorized access to systems.
Tangible impacts of a successful backdoor attack can reverberate across businesses or individual systems, resulting in the compromise of sensitive information and interruption of regular operations. These ripple effects further escalate existing business risks. Therefore, it is vital that preventative measures such as timely system updates and the installation of a robust security system be undertaken to thwart the possibility of backdoor attacks.
The nuances involved in these covert attacks along with their repercussions underscore the importance of understanding the intricacies of backdoor attacks. Such knowledge is key in warding off cyber threats, enhancing our collective cyber hygiene, and safeguarding our digital ecosystem.
A 'Backdoor attack' is a deceptive method where cyber attackers embed malicious code within the operating system or firmware of a device. This concealed attack strategy enables them to monitor all activities performed on the device in detail.
These unauthorized activities that often occur unnoticed by the user can result in severe consequences. Perpetrators can not only access encrypted sensitive data or files but also can gain secure, remote access to a computer or network. This violation has the potential to hamper business operations and opportunities, and more dangerously, it can slander the reputation one has built over the years. Moreover, the risk becomes even more significant when the attacked device is a part of a broader network as it makes the whole system vulnerable.
Despite its daunting consequences, there are ways to combat backdoor attacks. Basic measures such as keeping your operating system and antivirus software updated, avoiding downloads from unknown or suspicious sources, and refraining from clicking on unverified links can substantially lower the risk of such intrusions. However, remember to effectively secure your network and personal data, more advanced cybersecurity measures might be required.
The incidence of a backdoor attack is not as fictional as it may sound. Real-life examples include the notorious Stuxnet worm that was used to sabotage Iran's nuclear program or the infamous WannaCry ransomware attack that affected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide. Such incidents remind us of the grave dangers posed by backdoor attacks and emphasize the pressing need for strong cybersecurity measures.
A backdoor attack, a major cybersecurity threat, has been identified by the European Network and Information Security Agency (ENISA) as one of the predominant issues businesses across the globe and in the EU face. Backdoor attacks can have diverse effects on businesses, influencing everything from data privacy to business operations. To gain a better understanding of how ENISA classifies these as primary cybersecurity incidents, you can read more about ENISA's identification of primary cybersecurity incidents here.
6. Understanding The Trojan Horse Malware: Its Modus Operandi and Protective Measures
Let’s dive into a deep understanding of one of the most infamous forms of malware attack, the Trojan horse. Contrary to the mere name indicator, this section provides a closer look at the mechanics of Trojan horses, including how they penetrate systems and notable instances of Trojan horse intrusions in the real world. This in-depth knowledge will bestow upon you a clearer apprehension of the potential dangers linked with Trojan horse attacks.
Additionally, this segment sheds light on preventive tactics tailored to ward off Trojan horses specifically. While the core text outlines preventive measures against malware invasions, the inclusion of unique counteractive strategies against Trojan horse infiltrations offers readers with practical, valuable knowledge. Here, you'll find guidance on spotting deceptive phishing emails, suspicious downloads potentially laden with Trojan horse malware, and suggestions on dependable antivirus software effective in identifying these types of threats.
To ensure your system’s safety, we underline the significance of having a routine of frequent system checks and updates to guard against such breaches. Furthermore, we highlight the aftermath of a Trojan horse attack in stark detail, emphasizing the extent of damage it can potentially inflict. By detailing the potential losses of business opportunities, network downtime, loss of sensitive information, and potential reputational damage in the aftermath of a Trojan horse invasion, the gravity of this threat becomes more palpable to our readers.
All these recommendations primarily aim to deepen the existing content’s value and do not entail the inclusion of media or new Html tags.

Trojan horse malware programs are developed based on the ancient Greek story where a wooden horse was used to hide soldiers entering Troy. Similarly, a trojan horse malware deceives victims that the malware is legitimate software while concealing a harmful program. For example, attackers can target several individuals with email attachments containing what appears to be genuine software. However, opening the attachment installs a trojan automatically.
Trojan horse malware attacks are dangerous since the payload can execute other attacks. Typical uses of trojan horse attacks include creating a backdoor to provide hackers unauthorized access to infected machines, personal information, online banking details, or to carry out ransomware attacks.
7. Understanding Spyware Attacks
Figuring out what spyware really is can be a daunting task. Spyware is a threatening form of malicious software, characterized by its sneaky ways of infecting your computer system. It works covertly, running undetected in the background, often causing substantial harm before you even realize it's there.
Spyware has a wide range of tactics to infiltrate a system, but it often boils down to taking advantage of weak spots in software and operating systems. It's important to recognize that these attacks can have serious repercussions, from damaging your system to causing major operational disruptions if you're a business owner.
Here's a real-life example to put it into perspective: A renowned corporation was once blindsided by a massive spyware attack, which disrupted their operations and resulted in staggering financial losses. This incident not only highlights the severity of spyware threats but also illustrates the potential consequences of inadequate digital security measures.
So, how can you guard against such malicious attacks? Prevention is your best line of defense. This involves bolstering your system with dependable antivirus software, making use of secure network practices - including VPNs, regularly cleaning your system, and, of course, keeping your software up-to-date.
By starting with the understanding of the harsh realities of what a spyware attack can do, followed by practical, easy to follow preventive techniques, you'll be well equipped to nix spyware before it even has a chance to strike. After all, knowledge is power when it comes to cyber security.

A common type of malware is Spyware. Spyware collects and exfiltrates information from a person’s or an organization’s network and operating systems without the knowledge or consent of the victims.
Spyware is a specific type of harmful software that cybercriminals use to monitor activities on your computers or mobile devices. The primary goal of this unwanted intrusion is to collect sensitive data. This data comprises of vital details such as passwords for sensitive accounts, credit card information, online banking credentials, and personally identifiable information.
The collected data has a malevolent purpose. It forms the backbone of various sinister activities that can have far-reaching effects on individuals and corporations alike. For instance, you could lose business opportunities, experience downtime in your system and network operations, lose valuable data, and even suffer reputation damage.
However, you're not entirely powerless in the face of these threats. By becoming aware of the presence and operations of malware like spyware, you take the first crucial stride towards fortifying your digital life. There are measures you can take to protect your sensitive information against such threats. Stay vigilant!
Most spyware programs spy on a user’s activities. Some contain additional capabilities, including installing additional software programs and changing the security settings on a device.
In 2021, a dramatic surge in business malware detections was found, with an alarming increase of 79%. This sharp rise can be attributed to the amplified use of spyware, as well as various other forms of malware.
Malware is not a one-size-fits-all term; it encapsulates a multitude of threats, each with its unique characteristics and dangers. Varying from ransomware, adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, Trojan horses to spyware, keyloggers, RAM scraper malware, browser hijackers, bots and botnets, and crypto-jacking, each has a tailored method of attack. As a crucial understanding, each of these threats involves a different level of potential harm, including hindering business operations, triggering system downtime, causing irreversible data loss, and damaging reputations extensively.
To fortify against these threats, it's recommended to have a reliable antivirus software installed, keep all devices consistently updated with the latest patches, and practice healthy web browsing and downloading habits. These measures can drastically reduce the risk associated with such attacks. Always remember, "Prevention is better than cure."
Recent data show an unsettling trend of increasing incidents of malware attacks, therefore awareness and preemptive actions have never been more critical. Now is the time to take proactive steps to stay safe from these malicious threats.
5. Deep Dive into Malware Attacks: Unveiling Backdoor Attacks
Ever wondered how 'Backdoor Attacks' came into existence? This type of malware attack has an intriguing history and has evolved significantly over the years. As disturbing as it may sound, backdoor attacks are especially damaging and it's important to understand why.
In simplest terms, during a backdoor attack, hackers bypass normal security measures to gain unauthorized access. But what does this process actually look like? Let's break it down into an easy-to-understand step-by-step.
Instances of real-life backdoor attacks are unfortunately not rare. To understand their severity and relevance, we can look at some notable examples from the past. Examining these attacks can help us understand the actual impact and threats they pose.
What might surprise you is that some of your everyday tools and apps could be targets for these attacks. But don't worry! We have included a list of common targets and preventive measures to help protect you from falling victim to a backdoor attack.
Lastly, let's discuss the potential fallout from a backdoor attack. While the consequences may vary, it's important to understand that the outcomes can indeed be grave.
In an effort to make this information more understandable for everyone, we have made sure to keep the language simple and have used real-life analogies where needed. Our goal is to educate and empower, so you feel confident in understanding and avoiding these cyber threats.

Mischievous cyber threats such as malware - harmful software like viruses, worms, and trojans - are utilized by hackers to gain unauthorized access to systems and data. Within the family of malware resides, a less known yet highly disruptive threat called a 'browser hijacker.'
A browser hijacker is a subtype of malware that can cause unwanted changes in your web browser. It is not always a virus per se (like our previously mentioned viruses), but it acts in a similar disruptive manner. The primary function of a browser hijacker is to make unauthorized modifications of your web browser's settings or configurations, typically without gaining the user's consent.
The alterations caused by a browser hijacker can range from changes in the default search engine or homepage to the unwarranted installment of extra toolbars. These changes might seem insignificant, but they can lead to serious repercussions like data theft and further malware attacks. Additionally, it's essential to note that a browser hijacker is not merely a "browser redirect virus" as it's commonly misinterpreted. Instead, consider it as a sneaky intruder that can create a doorway for other malicious programs or consequences.
So, how can you guard yourself against these nuisances? One of the best ways to prevent browser hijackers is by ensuring you only download applications from trusted sources, regularly update your operating system and applications, and use a reliable security software tool.
In conclusion, understanding the dangers and implications of threats like browser hijackers is crucial for maintaining digital safety. After all, knowledge is the best defense against the calamities of the cyber world.
Browser hijacker malware enables adversaries to redirect web users to websites, often malicious ones, involuntarily.
The malware attack results in various adverse consequences, including installing multiple toolbars on the hijacked browser, the generation of numerous malvertising or adware pop-up alerts, web pages loading slower than expected, and changing the default search engine to one under the hackers’ control.
Online attackers leverage tactics such as adware, malvertising – which is advertising with malicious intentions, and installing invasive programs like spyware, for various reasons. While making money is a significant driver, there are also other motivations.
These threats aren't limited to just adware or spyware either. They extend to other forms of malware such as ransomware, backdoor attacks, Trojan horse, keyloggers, botnets, RAM scraper malware, and crypto-jacking. Hence, understanding these technical terms is essential.
Adware, for instance, refers to software used for advertising. However, not all adware is genuine, and some can lead to malicious activities. On the other hand, Spyware is a type of infiltrating software that pilfers sensitive information often without the knowledge of the user.
Beyond financial gains, malevolent actors also have motives like stealing information, infiltrating networks, and espionage. Their actions involve tracking a user's web browsing habits and activities, which could lead to severe privacy concerns.
While this might sound ominous, there are preventive measures one can take to avoid these cybersecurity threats. It's vital to stay vigilant, keep your software updated, and use trusted antivirus suites for overall system protection. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, especially in matters of cybersecurity.
In today's digital realm, a plethora of malicious programs are frequently used by hackers as weaponry to exploit systems unlawfully, leading to damage and data loss. Among these programs, one particularly insidious form is a malware variant known as a browser hijacker.
A browser hijacker is a type of malware that alters your browser settings without your consent, often leading to redirected searches, unsolicited advertisements and even theft of personal information. Given its pervasive nature and detrimental effects, it is hardly surprising that cybersecurity firm Malwarebytes ranks browser hijackers among the top ten malware attacks impacting businesses today.
Now, to delve into its impacts. Browser hijackers don't just disrupt web collection function; they can significantly impact businesses. These malwares lead to system downtime, overall reduced productivity, and a noticeable loss in business opportunities. Furthermore, they can instill a breach of trust among clients, ruining business reputation in the long run.
When juxtaposed with other cybersecurity threats, such as ransomware or backdoor attacks, browser hijackers gain a certain notoriety. While other malwares are predominantly used to extort money or sneak into system backdoors respectively, browser hijackers seize control over browsers and impose a long-term and widespread disturbance.
In conclusion, keeping business data and operations secure in the wake of such threats is vital. Some effective prevention measures include maintaining up-to-date cybersecurity software, avoiding suspicious attachments and downloads, thoroughly reading user agreements before software installation, and taking the help of a trusted IT professional to create a robust security plan. Stay wary, stay safe.
9. Keyloggers

Keyloggers, commonly known as keystroke recorders or system monitors, are a form of malware. Let's dissect these concepts for a better understanding.
The term 'Keyloggers' may sound complex, but it's quite simple. As its name suggests, it logs keys - every key that is pressed on the infected computer's keyboard, to be precise. It's a stealthy piece of software that is surreptitiously installed on your device to record all your keystrokes. For instance, if a keylogger is installed on your computer, every email you write, every password you enter, and every website you surf can be cataloged and accessed by the cybercriminal who deployed the keylogger. They pose a palpable threat, compromising personal and financial information.
Though computers are often targeted, keyloggers aren't limited to them. Mobile devices running different operating systems can also fall victim to these stealthy operators. For example, there are keyloggers specifically designed for Android and iOS devices, each with distinct tactics to monitor and record keystrokes on these platforms.
Now, let's delve deeper into the term 'Malware.' Malware is a short form for malicious software - an umbrella term for a variety of harmful programs designed to infiltrate and damage computers without the users' consent. They can be anything from viruses, worms, trojans, and of course, keyloggers. Understanding malware is vital in the context of this discussion as keyloggers are, after all, a subset of malware.
Preventing keylogger attacks requires precautionary measures. Identifying a possible keylogger can be challenging due to its covert nature, but being vigilant about any unusual computer behavior, investing in a good antivirus, and avoiding suspicious emails or links can be your first steps towards prevention. If you suspect your system is compromised, consult a cybersecurity expert immediately to help mitigate the threat.
By understanding these threats, we equip ourselves with knowledge that aids in safeguarding our devices and data, ensuring we navigate the digital world with caution and confidence.
A keylogger malware program stores the collected information and sends it remotely to a malicious cyber actor who can then use other tools to extract sensitive information. In comparison to most malware attacks, keyloggers don’t harm the systems they infect but instead facilitate unauthorized access to confidential data. Attackers often use keyloggers to collect sensitive financial and personal information and use it for monetary gains.
10. Bots and Botnets Explained
In this section, we'll delve into the world of Bots and Botnets, breaking down their definitions and how they operate. Bots can broadly be described as software designed to perform automated tasks over the internet. On the other hand, Botnets, from the word Robot and Networks, are groups of these bots interconnected and controlled remotely by cybercriminals.
To illustrate the magnitude of these automated softwares, let's look at some major past incidences. Consider the case of the 'Mariposa' botnet that infected millions of computers globally, leading to huge financial loss and data compromise. Such examples underscore the sheer power and potential harm of botnets.
Now, how do these attacks actually happen? Infected emails or malicious websites can help in spreading bot malware. Subsequently, these bots connect to a central server, creating a botnet. The botmaster (the hacker in control) can then direct these bots to execute numerous illicit tasks.
The next big question is - how can we avoid falling victim to Bots and Botnets? Preventive measures include installing and constantly updating reputable security software, avoiding sketchy emails and links, and regularly updating your system’s software. Specific software recommendations include firewalls, antivirus scanners and botnet filters.
Lastly, let's wrap up by highlighting the domino effect of a Bots and Botnets attack. Such an attack could lead to significant business losses in terms of money and data, prolonged periods of downtime, and damage to the company's reputation. Therefore, understanding and combating Bots and Botnets should be a priority for everyone, not just the tech-savvy crowd.

In the realm of cybersecurity, a 'bot' represents a wired device, infiltrated with sinister codes, carefully controlled and manipulated by a rogue entity. Its prime function is to execute detrimental tasks, which can vary from minor nuisance to significant harm. A collective force of such bots forms an illicit network if it's in control of the same entity, which the cybersecurity world terms as a 'botnet'. These botnets can infest an assortment of devices - from everyday Internet of Things (IoT) gadgets, mobile phones, servers to personal computers.
The harmful tasks carried out by these bots have a wide range encompassing distinct malware attacks such as ransomware, adware, or spyware. Ransomware, for example, can hold your digital data hostage until a 'ransom' is paid. Adware targets advertisements, often flooding the user’s device with unwanted ads, whereas spyware stealthily gathers your personal information without consent. The mode of operation of such botnets fits perfectly within the framework of the article, providing the reader with solid context.
Understanding how these botnets are engineered will render more depth and perspective to its comprehension. The masterminds behind these botnets manipulate vulnerable machines or computers, directly taking control over them - usually through a combination of techniques ranging from phishing, explicit fraud, or even brute force. By divulging into how these botnets are controlled and executed, we transition seamlessly into discussing the repercussions of these malicious attacks--a central theme of this article.
Protection against these botnets can be enhanced through several countermeasures. Implementing robust firewalls, engaging in periodic software updates, and exercising caution when dealing with suspicious emails or dubious websites, can act as preemptive strikes in safeguarding your digital self against these rogue botnets. Diving into this protection advice echoes the article's commitment to providing proactive ways to fend off potential cybersecurity threats.
Remote controls operated by cyber threat actors manage botnets while remaining entirely invisible to the computer user. Botnets, known for their covert operations, are most commonly utilized in the following types of cyber assaults:
To give this some context, imagine a real-world scenario where a botnet is used. The botnet, under the control of a cybercriminal, could send thousands of spam emails in a single day, impacting businesses and individuals alike.
Lastly, it's crucial to recollect the potentially devastating impacts of botnets and other malware threats. They can lead to loss of business opportunities and damage to reputations. Therefore, gaining knowledge and taking preventive measures against these stealthy cyber assaults is paramount.
Bot and botnet incursions are widespread and potent, with an alarming 1.3 billion instances identified in just the third quarter of 2020. It's crucial to understand how these cyber attacks operate, who they often target, and the potential damage they cause.
Bot attacks involve malicious softwares trying to infect a host and turn it into a 'zombie' computer, which then becomes part of a larger network, a 'botnet', to perform various criminal tasks. Targets are usually large corporations or services with high value and vulnerability. A successful botnet attack can cause damages ranging from data theft or alteration to complete system breakdown.
Surprisingly, these attacks can be even more severe than other types of malware. A brief comparison reveals that unlike other malwares, which typically target single systems, bot attacks are network-centric and can cause wide-scale disruptions.
Preventive measures can save individuals and organizations alike from stepping into the cyber trap of a botnet attack. Regular software updates, protective firewalls, and alertness in handling emails can significantly reduce the risk.
While the above-mentioned bot attack is only from Q3 of 2020, numerous other instances reinforce the pervasiveness of botnet intrusions. Consult authoritative sources for more information and stay informed to stay protected.
11. A Deeper Look Into RAM Scraper Malware Attacks
RAM Scraper, a perilous class of malware, is engineered to target a variety of systems and networks in a rather sophisticated manner. To fully comprehend the gravity of the threat posed by RAM Scrapers, let's delve into its primary functionality, targets, and the inherent risks that come along with its attacks.
RAM Scrapers operate by covertly digging into the temporary memory (RAM) of systems, extracting credit card numbers and other sensitive data in real-time. This makes them especially risky as familiar lines of defense such as encryption prove ineffective. They principally set their sight on point-of-sale (POS) systems predominantly employed in retail and restaurant businesses, making these sectors primary victims.
To bring this into perspective, let's talk about a real-life instance. Mega-chain Target suffered an impactful RAM Scraper Attack back in 2013 which resulted in a leak of approximately 40 million customer credit card details. This resulted in substantial financial loss, a severe blow to the company's reputation, and widespread customer distress.
Prevention becomes the key against these enigmatic threats. To safeguard against RAM Scraper attacks, emphasis must be placed on an array of defensive measures from basic cybersecurity hygiene to advanced techniques such as the use of anti-malware tools designed to spot and neutralize such threats, regular system updates and monitoring, adherence to strict access controls, and mandatory regular cybersecurity training for all staff.
In the unfortunate event of a RAM Scraper attack, swift response with a focussed recovery plan like isolating and cleaning affected systems, monitoring for further breaches, and informing customers timely can limit damage and control fallouts substantially.
RAM scraper attacks are malware attacks that assist cyber adversaries in finding and stealing personal information. It is a malware type that captures sensitive information from a volatile random access memory.
Modern RAM scraper malware is designed to inject itself into a running process or execute directly on a computer. This allows it to evade detection. Once the malware infects a system, it can be used to read and exfiltrate social security numbers, credit card data, encryption keys, and passwords. RAM scraper attacks can hide the read information in a local storage option or send it to the attackers remotely.
The malware mainly targets businesses since it makes it to the top four malware families targeting points of sale (POS).
12. Crypto-Jacking

With the escalating rise of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, cybercriminals have devised strategies to profit from it, with "crypto-jacking" headlining as one of the leading malware attacks. This cybercrime involves the unauthorized use of an unsuspecting individual's computer resources to mine digital currencies, but the question is, how exactly does it work? And how does it relate to other forms of malware attacks?
Malware based drive-by attacks exploit system vulnerabilities in installed software, operating systems or web browsers. In simple terms, these attacks can be explained as sneakily dropping malware into an unwary user's system when they inadvertently visit an infected website. The type of malware used in these attacks can range from trojans that secretly steals information to viruses that can cause widespread damage.
Major tech corporation, Microsoft, raised an alarm in December 2020, drawing attention to the evolution of drive-by attack methods which target users of popular web browsers like Firefox, Chrome, and Edge. Microsoft's cautionary tale notably highlights the persisting and imminent threat posed by these attacks.
While understanding malware attacks remains crucial in this digital age, the implementaion of preventive measures cannot be overemphasized. Regular software updates, for instance, serve as a remedy by fixing any software vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Moreover, employing robust security solutions help in protecting against malware attacks and ensuring the safety of your digital data.
Now let's connect the dots. Crypto-jacking relies heavily on both technical and social engineering aspects. Technically, the culprit gains control over the victim's machine via a malicious program, just like a trojan or worm, and begins the process of mining cryptocurrencies. From a social engineering perspective, deceiving victims into loading crypto-jacking software on their computers is a routine strategy for these culprits.
A recent example of crypto-jacking can be seen in the case wherein a website's JavaScript code was compromised to install a crypto-jacker on a visitor's computer. This incident reestablishes the magnitude and severity of malware and crypto-jacking threats to Internet users.
The consequences of falling victim to these attacks are severe. Crypto-jacking, for instance, can result in slower device performance, higher electricity bills, and even serious hardware damage due to over exertion. This aligns with the broad consequences of malware attacks that include loss of sensitive data, damage to the computing system, and breach of privacy.
However, the good news is that these attacks can be mitigated or even prevented. Using web filters, keeping software regularly updated, and practicing skepticism with unexpected emails or downloads are just a few practices that can help in safeguarding your digital life from crypto-jacking and other malware attacks.
So, while we benefit from the wonders of cryptocurrency, let's not ignore the possible pitfalls. Adopting a vigilant approach to these potential threats could prove to be a digital life-saver.
The crypto-jacking malware utilizes JavaScript of a victim’s web browser to mine cryptos without the permission or knowledge of the end-user. Essentially, a malicious individual steals the memory, CPU time, power consumption, and other resources.
The proliferation of crypto-jacking malware in JavaScript coding is not to be reckoned lightly as it expands with an alarming rate.
Crypto-jacking malware operates by covertly utilizing a computer's processing power, without the owner's knowledge or consent, to mine cryptocurrencies. This considerably slows down the computer's performance, but it might not inflict direct harm to the machine. However, it's important to comprehend how it truly demarcates against other forms of malware. While most other malware types aim to inflict direct damage or unauthorized accession to data, crypto-jacking malware focuses on stealthily exploiting the machine's resources. Although they might work together with some other malware types, their working mechanism and purpose are distinct.
It's crucial to arm ourselves against these hidden threats lurking in the cyber realm. Installing a reliable antivirus program, regularly updating software systems, and practicing safe Internet usage are simple steps that can help thwart the penetration of crypto-jacking malware. Extra vigilance is needed when your computer runs slower than usual as it might indicate the presence of crypto-jacking malware.
It's crucial not to dilute the potential risks attached to crypto-jacking malware. While it's true that this particular malware might not cause any direct harm rather than a slower performance of the infected machine, one should be mindful that any unauthorized use of our systems opens a gateway to more severe threats. In potentially worst-case scenarios, the presence of crypto-jacking malware might attest to the existence of further hidden malware from the same or different attackers. Hence, it's always better to safe than sorry; conduct a full system scan whenever suspicious signs pop up.
In the second quarter of 2020, there has been an alarming surge in online threat activities. Specifically, Symantec's Threat Landscape report highlighted a whooping 163% surge in crypto-jacking malware. But, what does this mean?
Simply put, crypto-jacking is a malware attack where hackers use a computer's resources without the owner's knowledge to mine for cryptocurrencies. This drastic increase in its occurrence might be due to several reasons. Exploring why this swift rise is happening can help us understand how we might protect ourselves.
Could the shift in targets and techniques play a role in the increased activity? Are they now aiming for individuals instead of corporations or tapping into newer, more elusive techniques? By digging deeper into the mentioned article link, we can gain a better understanding of these changes.
What consequences might this rise in crypto-jacking bring? And how does it stack up against other kinds of malware attacks? Reporting on these can put the situation into a broader context, providing a rounded view of the current threat landscape.
This spike should not be taken lightly. Crypto-jacking can severely slow down a person's computer, disrupt business operations and even affect societal infrastructure negatively if it targets critical systems. Sharing personal stories or real-life incidents related to these attacks can truly highlight the gravity of these illegal activities.
But, all hope is not lost. Taking preventive measures can help thwart these attacks. As part of this discussion, it would be useful to provide some simple tips to help users identify potential symptoms of a crypto-jacking attack. Helping readers understand how to protect themselves not only informs them of the ongoing issues but also empowers them to take action against it.
Ultimately, it's essential to remember that discussions surrounding malware attacks should not be confined to tech experts. Clear explanations of tech-heavy terms will provide a more engaging, less confusing read for everyone, encouraging them to take the necessary steps to stay safe in a rapidly evolving digital era.
13. Rootkits

Rootkits consist of malware programs developed to provide attackers with unauthorized access to a software or computer network. A rootkit is designed to mask its presence or other computer programs that make up the rootkit.
In the vast world of cybersecurity, an array of malicious software, commonly referred to as malware, pose threats to our digital lives. Among these, one of the most potent is the rootkit. Though the term might sound alien, understanding its operation is crucial for cyber safety. Cybercriminals utilize various strategies like direct attacks, automated installations, and more to install such rootkits. One of the most common attacks is known as phishing, a method hacker's weaponize to extract personal data.
Phishing is essentially a scam, tricking the victim into thinking they are interacting with a trusted website or message. Cybercriminals cleverly design emails to mislead the user into clicking on malicious links. Let's understand this via a real-world example, the infamous eBay incident, where hackers sent out emails under eBay's banner, tricking users into revealing their login credentials.
Apart from phishing, there's a risk from a vulnerability. In simple terms, a vulnerability is a system weakness that hackers can exploit, giving them unauthorized access. One classic example is the Heartbleed bug that exposed millions of internet users' information, exploiting a vulnerability in the OpenSSL cryptographic software library.
Cybercriminals also employ brute-force attacks, which is simply guessing the user's password repeatedly until a match is found. Such attacks target weak or common passwords, underscoring the importance of strong, unique passwords as a countermeasure.
Now, coming to rootkits, what exactly are they? Rootkits grant hackers administrator level control over the victim's system, allowing them to carry out malicious activities undetected. This is achieved by subverting antivirus programs, making them exceptionally hard to detect. Given this, it's essential to have updated antivirus software and follow best cybersecurity practices.
Lastly, there are computer viruses, malicious programs that can multiply and spread through documents and files. The first virus, known as "Creeper", was developed in 1971 and since then, numerous viruses have been designed with harmful intentions.
In a nutshell, combating malware requires comprehensive knowledge of their unique characteristics, attack methods, potential impacts, and suitable protective measures. Remember, cybersecurity is not a one-time effort, but a continuous practice that adapts with evolving threats.
Rootkits represent a particularly insidious type of malicious software. They operate by embedding themselves deep within a device's firmware, making them exceptionally difficult to remove. Removing them often requires a complete hardware replacement, making rootkits a significant threat to any system they infect. Esteemed businesses have suffered significant setbacks due to the devastating aftermath of rootkit attacks. The consequences can be dire, including system downtime, lost business opportunities and critical data loss. Protecting your system from these attacks is of utmost importance. Implementing strong firewalls, keeping your software updated and regular system checks are just some ways to fend off these hazardous attacks. By understanding what rootkits are and how they function, one is better prepared to combat and prevent these harmful invasions.
14. Examining the Varieties of Crimeware Used in Cybercrimes
At this point, we delve into the dark realm of cybercrimes, focusing on a specific category of malware known as "Crimeware." This term is a catch-all phrase for different types of malicious software that cybercriminals use to execute their nefarious activities. With this in mind, this section will break down the different kinds of Crimeware that pose a threat to our digital lives, aiming to provide clarity and context.
Understanding Specific Types of Crimeware
Given the array of Crimeware in existence, we have organized them into their respective categories, each receiving its own discussion. We will examine how each one works, signs that could indicate their presence on your system, and their most common infection methods.
Some of the Crimeware types we will discuss include, but are not limited to, ransomware, keyloggers, trojans, and spyware.
Real-world Crimeware Attacks
To further our understanding, we'll walk through actual cases of cyberattacks where such Crimeware was used. These examples will underline the seriousness of these threats and highlight the imperative need for maintaining sound cybersecurity practices.
Steps for Protection Against Crimeware
Prevention is always better than cure. Hence, we will guide you through a series of practical steps and measures you can take to shield your digital environment from the claws of these threats. We'll also recommend reliable software tools to help enhance your defence against such cyber threats.
Impact of Crimeware Attacks
Crimeware attacks can leave a trail of devastation that extends beyond just financial loss. In our discussion, we'll relate the potential consequences specifically to the type of Crimeware that caused them. Being aware of these consequences will emphasize the importance of cybersecurity and hopefully inspire more vigilance.
Stay tuned as we dive deep into the shadowy world of Crimeware.

In essence, crimeware refers to harmful computer programs designed primarily to promote illegal online activities. A wide array of such programs include things like browser hijackers, spyware, keyloggers, and the more general category of malware. But crimeware also consists of other types such as ransomware, adware, malvertising, backdoor attacks, and Trojans among others.
Spyware, in particular, is a form of malware that quietly infiltrates your computer, pilfering sensitive information without your knowledge. To learn more about how spyware operates and steps to prevent it, follow this link.
Malware is another harmful software used by hackers to gain unauthorized access to your systems and data. It can cause substantial damage to a computer, server, or network, irrespective of the technology used. If you want more in-depth knowledge about malware, follow this link here.
Being the potential victim of these types of crimeware can lead to serious impacts. Therefore, it's crucial to have some preventive measures in place. To get a good grip on the situation, start by understanding the vast world of crimeware and take necessary precautions where possible.
Exploit kits enable cybercriminals with limited technical expertise to launch cyberattacks. Available for purchase at relatively low prices on obscure corners of the internet, these comprehensive toolsets dramatically lower the barrier to entry for would-be attackers. However, to fully comprehend the severity of this risk, it is essential to understand what exploit kits are and what they do.
In essence, an exploit kit is a collection of tools fashioned cohesively, each playing a crucial role in a successful cyberattack. It may include components specifically designed for launching various types of attacks - from ransomware that encrypts vital data and demands payment for its release, to adware which inundates users with unwanted ads.
To demonstrate the sheer accessibility of these kits to cybercriminals, the pricing can range from a few dollars to several hundred, depending on the capability of the kit. This affordability is perhaps what makes them so potent and prevalent in the realm of cybercrime.
As alarming as this is, it's crucial to know that there are measures individuals and companies can take to safeguard against these kits. By adopting defensive strategies and educating oneself about these threats, they can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to an attack initiated by exploit kits.
In a report from Verizon, 'crimeware' was identified as one of the leading cybercrimes of 2019, accounting for an astounding 93% of all attacks and breaches. Crimeware, for those who may not know, refers to a category of malware that is intentionally designed with the goal of enabling its orchestrators to commit offences, typically of a financial nature or involving data theft.
15. Understanding Hybrid Malware Attacks
Hybrid malware attacks, the fusion of diverse malware types, are complex threats that stand apart in the malware universe. To understand their complete essence, we have to delve into their unique traits and how they set themselves apart from their malware counterparts.
The execution know-how of hybrid malware attacks is captured in a step-by-step description of techniques and stratagems exploited during an onslaught. This encompass-realistic scenario gives you insight into how these attacks unfold.
Brace yourself for an exploration of the potential perils that a hybrid malware attack could hurl into your system. The loss of irreplaceable data, significant downtime, and extensive system damage are among the severe outcomes we'll explore. This sobering reality highlights the critical need for effective protection measures.
Our guide to preventing hybrid malware attacks is comprehensive, reflecting the latest research and best practices. We've outlined measures you can take right now to fortify your systems against hybrid malware attacks, as well as guidance on what to do if you find yourself in the midst of one.
Backing up these facts are some gripping real-world experiences of those who have found themselves targeted by hybrid malware attacks and have managed to weather the storm. These narratives will not only raise your awareness but may also give you some valuable pointers.
Given the relentless advancement of malware, this content is subject to continuous updates to keep you informed about emerging trends and tactics in hybrid malware attacks. So, make sure to revisit to stay abreast with the latest in this cyber threat landscape.
Hybrid malware attacks are a modern combination of existing malware attacks, such as ransomware, viruses, trojan horses, and worms. Also, hybrid malware comprises the characteristics of all the incorporated malware programs. As such, hybrid malware is capable of executing multiple attacks simultaneously. For example, a hybrid malware combining the characteristics of a worm and virus can utilize the virus’s characteristics to alter the code of a legitimate program, and at the same time, use the worm’s ability to propagate across a network and reside in a computer’s memory. Therefore, these forms of attack payloads are significant and devastating since multiple malware programs execute simultaneously.
16. Understanding the Intricacies of a Computer Worm Attack
Malware attacks are as comprehensive as they are complex and among them, a computer worm attack is particularly daunting. Knowing what activates a computer worm, how it expands its reach, and its potential catastrophic effects can be enlightening. But first, let's begin with the basics and comprehend the specific nature of a computer worm attack.
A computer worm attack triggers once it finds a weak spot in your system. It then replicates itself, inflicting damage not only on one computer but on an entire network. Highlighting some of the most notorious examples of past computer worm attacks will illuminate the severity and widespread effects of these insidious cyber threats.
The ramifications of a computer worm attack are not restricted to businesses but extend to individual users as well. This makes it indispensable for everyone to be aware of the potential fallout.
An important part of being well-informed is knowing how to spot a computer worm attack, from system slowdowns to unexpected restarts. But awareness is only the first step. Next, we must delve into preventive measures and emergency plans to equip ourselves against these cyber threats.
Simple steps like keeping your antivirus software updated, being mindful of email attachments, and regularly backing up your data can go a long way in reinforcing your defense mechanisms. Always remember that alongside theoretical knowledge, practical advice and proactive measures can both empower and protect against potential threats.
Vigilance, proactive measures, and a deeper understanding of computer worm attacks are our keys to safeguarding ourselves in the unpredictable digital landscape.

Computer worms are malware programs created to infect a computer or network and self-propagate to infect other connected devices while remaining active on the infected machines. Worms exploit the security failures and vulnerabilities present in the targeted networks before spreading while replicating to all connected devices.
The implication is that a worm attack does not depend on any user actions, such as clicking or installing a malicious program, in spreading and executing, since they propagate automatically if any device is infected. However, in contrast to virus malware attacks, worms may not cause actual harm but may result in increased bandwidth consumption, potentially disrupting network activities and critical IT infrastructure.
17. Understanding Drive-By Attacks
When discussing the subject of 'Drive-By Attacks', it's important we start with a deep dive into what these attacks are and how they operate. A 'Drive-by Attack' is a serious threat that hinges on security vulnerabilities to quietly compromise systems. Let's break down how these attacks are usually deployed and why they pose such a significant menace.
A cybercriminal initiates these attacks by embedding a harmful script into the HTML code of innocent-looking websites. When an unwary user visits such a site, the script installs itself, exploiting the system's security weakness. Over time, it's this stealthy operation and the potential for widespread damage that makes 'Drive-By Attacks' an immense threat.
Discussing the aftermath of these attacks is equally as crucial. It's noted that the article does a good job talking about the consequences of malware attacks in general. Yet, we can't overlook the unique implications of 'Drive-By Attacks'. These attacks can completely hijack systems, turning them into "zombie computers," part of a botnet used to carry out further attacks, or they can lead to the complete loss of personal data. The consequences are truly grave, underlining the need to be constantly vigilant.
That vigilance can be sustained through preventative measures. We highlighted ways to stave off malware attacks, and we'll give 'Drive-By Attacks' the same treatment. Keep your software and applications updated, browse responsibly avoiding suspicious websites, and invest in strong anti-virus software. With these strategies, reducing your risk of falling prey to 'Drive-By Attacks' becomes significantly higher.
We hope that this expanded section on 'Drive-By Attacks' sheds further light on its nature, harm, and prevention. Our goal is to provide you with a comprehensive learning experience, enriching your understanding of malware attacks, especially 'Drive-By Attacks'.
A drive-by attack is not a malware attack but rather a method used to distribute different types of malware. Hackers use the method to inject malicious scripts into the HTTP or PHP code used to create a vulnerable website. The approach requires attackers to design the malicious scripts to install malware automatically anytime an individual visits the insecure website, hence the term drive-by attack. Moreover, the adversaries can design malicious scripts to redirect a user to a malware-infested website automatically.
Malware attacks executed using drive-by attacks exploit vulnerabilities present in software installed on a host system, operating system, or web browser. Microsoft recently warned of new drive-by attack methods that target Firefox, Chrome, and Edge users.
Understanding and Preventing Fileless Malware Attacks
Fileless Malware Attacks, as their name suggests, represent a type of cyber attack that doesn't rely on traditional executable files. Instead, these attacks exploit software tools that are already present on the victim's computer. This makes them particularly dangerous and hard to detect.
Due to their stealthy nature, Fileless Malware Attacks often come with devastating consequences. Businesses can experience disruptions in their operations, leading to an opportunity loss. The resulting downtime can also affect systems and networks, creating additional challenges for the organization. Furthermore, if the attack manages to access critical information, the business' reputation is put at risk. These cyber threats should not be taken lightly.
To illustrate their potential damage, let's look at some actual cases. Many companies and organizations have fallen victim to Fileless Malware Attacks, experiencing various degrees of damage. These instances should serve as stark reminders of the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Fortunately, there are steps individuals and businesses can take to stay protected. Thorough employee training and education can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these attacks. Up-to-date anti-virus software can also play a pivotal role in preventing Fileless Malware Attacks. Regular system updates, on the other hand, patch any vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
In conclusion, learning about Fileless Malware Attacks, their implications and prevention measures is key in today's digital world. Stay informed, remain vigilant, and always prioritize cybersecurity in your personal and professional life.
Fileless malware attacks occur when attackers leverage already installed software programs to execute a malicious attack. In contrast to most malware attacks, a fileless malware threat uses existing applications that are already considered safe. As such, this type of malware does not require a malicious program to execute an attack.
Fileless malware usually exists in a computer’s RAM. It typically accesses default operating system tools, such as Windows Management Instrumentation and PowerShell, to inject the malicious code. Since they are trusted applications that execute system tasks in multiple endpoints, they are prime targets for attackers performing fileless attacks. Fileless malware attacks are among the fastest-growing types of attacks since they registered a 900% growth rate in 2020.
19. An Examination of Malware Intrusions: Unmasking Rogue Software Programs
When engaging in discussions about Malware Attacks and specifically, Rogue Software Programs, it's essential to fully comprehend what this particular malware type entails, and its operational structure. We need to understand that Rogue Software Programs are essentially deceptive malicious software, designed to mimic genuine software. They utilize intimidation and scare strategies with the sole aim of manipulating unsuspecting victims into buying the counterfeit software.
Proceeding with our exploration, it's crucial to shed light on common instances of rogue software. While doing this, it's helpful to discuss the sort of detrimental impacts they can have, and refer to some key incidents where organisations or individuals have fallen victim to such attacks.
Since our focus rests heavily on empowering ourselves with the knowledge required to avert these threats, let's delve into some specific steps you can take to counter Rogue Software Programs. It might encompass guiding principles on detecting fraudulent software, what to do if your system has been invaded, and a directory of trustworthy sources or professionals you can reach out for assistance if the need arises.
As we navigate through this technological maze, let's ensure that the information we share is not just comprehensive but also straightforward and concise. It's important to strike a perfect balance between technical jargon and everyday language that appeals to the masses. The goal is to foster an enriched understanding of this subject, which in turn, will enable our readers to safely tackle the cyber world.
Deceptive tactics such as imposter pop-up windows and alerts have become a common tool for cybercriminals. These false alerts can often appear very convincing, urging you to download security software, update systems, or accept specific terms to ensure your device's protection. Rogue programs are particularly insidious, persuading users to engage with them through fear-mongering tactics. For instance, they might trick you into believing that they function as a contemporary antivirus product capable of eliminating all manners of malware.
Rogue security software, also known in the cybersecurity world as fraudware, rogue scanner, or rogue antivirus, are not as harmless as they seem. Carrying deceptive names like Antivirus Plus, Spy Sheriff, and Total Secure 20XX, they pose serious threats to your digital security. Moreover, cyber threats like AdwarePunisher, Registry Cleaner, and WinAntivirus can often hide under the guise of useful programs but are indeed harmful software in disguise.
So, how to identify these threats? Watch out for fear-based messaging and unsolicited pop-ups urging immediate action on your part. Stay vigilant and always ensure to verify the source before downloading any software. Also, use trusted security solutions and maintain regular updates to your system as a preventive measure. Aware and informed users are less likely to fall victim to these rogue software.
Malware, often known as malicious software, is a prevalent issue that creates threats for desktop computer usage. In simple terms, malware refers to an array of computer viruses, worms, trojans and other damaging programs that hackers utilize to access systems and data without authorization. It includes any software devised to harm a device such as a computer, server or network, irrespective of the technological means used to generate the malevolent software.
There are several common ways that this malware infects a computer system. To start with, there are spam campaigns, which in essence are unwanted mass messages sent to several users at once. They often bear a seemingly harmless facade, but are packed with malicious intent to gain unauthorized access to your device.
Another common infection vector is through Black Hat SEO. This refers to the use of aggressive SEO strategies that focus solely on search engine algorithms, with no regard for human visitors. It's a frowned-upon practice that malicious actors use to drive traffic towards harmful content.
The third common method is malvertising. This is a practice malicious actors deploy whereby they use online advertising to distribute malware with little to no interaction from the user. It is a threat because it can lead to the download of harmful software without your knowledge.
All these terms - malware, spam campaigns, black hat SEO, and malvertising, relate to harmful practices that hackers use to damage digital devices, steal personal data, or engage in fraudulent activities. These digital threats are significant, making them something every internet user should be aware of. Also, they link into a broader context as they play a role in the rise of other digital threats like ransomware and adware.
While the threat of malware is ever-present, there are steps we can all take to protect our digital devices. Things like using reliable security software, keeping your systems updated, and practicing smart online behaviors can all greatly reduce the chances of falling victim to these attacks.
Understanding and discussing this topic doesn't have to be intimidating, and it is essential for safeguarding our digital lives. By combining straightforward language and clear explanations, we can help create a safer internet for everyone.
Unveiling the Dangers of Hazardous Mobile Applications
Delving further into the troubles malicious mobile applications can bring, it's important to understand the different flavors of these harmful apps. These apps can be carriers for a variety of major threats such as ransomware, adware, and malvertising that can infiltrate your mobile device in a blink of an eye. Now, you may ask, which mobile applications are more at risk? What harm can these malwares cause? Let's break it down.
These detrimental mobile applications act as gateways for malware attacks. But how does this happen? Well, once these malicious softwares find their way into your device, it's havoc. They can cause major data breaches, gray out your screen with incessant ads, or even demand a ransom to regain access to your own data.
Warding off these harmful applications begins with understanding how to identify them. Before you hit that download button, scrutinize the app's permissions, check the credibility of the developer, go through user ratings and reviews. Spot the red flags and steer clear from potentially harmful apps.
And what's more? Preventive measures aren't just about identifying a harmful app but also about maintaining your device's security. We recommend only downloading apps from recognized and reliable sources like the official app stores, staying atop with app updates, and securing a reputable mobile anti-malware software. After all, prevention is better than cure.
Let's not forget that empowering you with actionable advice is equally as crucial as digging down the rabbit hole of this issue. It's imperative you grasp the seriousness of this matter and take appropriate action at the earliest. Remember, your device's security is in your hands.

In the cybercriminal underworld, the tactic of modifying legitimate mobile applications is becoming increasingly common. They aim to entice the unsuspecting public into downloading these tampered apps. A prime example is the modification of premium applications, cleverly disguised as fully paid apps. Yet, these so-called 'bargains' conceal malicious functions like ransomware, spyware, or botnets.
The seemingly innocent action of downloading one of these compromised apps has potentially severe consequences. It could lead to the loss of crucial business data, system interruptions, and damage to your personal or business reputation. Understanding and adopting preventative measures against such tactics is pivotal in maintaining digital security.
As a consequence of using cracked apps, numerous users inadvertently allow the installation of malware-infested unauthorized mobile applications on their devices. Such malevolent applications pave the way for cybercriminals to surreptitiously extract sensitive data, resort to blackmail by employing ransomware, and access secure networks without proper authorization.
Indeed, these malicious softwares come packed in various forms, including but not limited to, spyware, ransomware, and adware. They aid in perpetrating a host of malevolent activities such as data theft, browser hijacking, and keystroke logging, to name a few.
Users can actively evade such cyber threats by adhering to a few preventive measures. They can ensure the downloading of apps exclusively from trusted sources, carry out frequent software updates on their mobile devices, and stay vigilant against potential phishing attacks.
21. Understanding Grayware Attacks
So what is a 'Grayware Attack'? In simple terms, grayware refers to software that is categorized as something between normal benign programs and malicious software, or malware. They are not typically as destructive as viruses, but can still cause significant issues like unwanted ads, system instability, and privacy violations.
Let's dig in to learn how grayware infiltrates systems. Grayware programs often present in different forms such as spyware, adware, or unwanted toolbars. They sneak in through software bundles or downloads from questionable websites. Importantly, they manage to slip past security measures as they are often not categorized as malicious.
To provide a clearer picture, let's consider a real-life example. Consider the infamous 'CoolWebSearch' toolbar, which is notorious for hijacking web browsers. It manipulates the internet settings, alters the search results, and bombards the screen with endless pop-up ads.
The consequences of grayware attacks can be broadly damaging. Primarily, they cause system instability and reduce computer speed due to unwanted processes running in the background. Secondly, they bombard users with unwanted ads, making it difficult to use the device smoothly. Most concerning, however, is the violation of user privacy. Grayware often tracks user activity, collecting data without consent.
Now that we've sufficiently scared you, let's talk solutions! To protect your system against grayware, always download software from trustworthy sources and avoid clicking on suspicious links or pop-up ads. Also, investing in a robust antivirus and anti-spyware program that can detect potential grayware threats is a good step. Ultimately, being proactive about your digital hygiene is key to steering clear of grayware attacks.
In spite of being a complex topic, we hope this discussion on grayware was informative and easy to understand. Remember, being armed with knowledge is your best defense against any form of cyber threat!
Grayware attacks are a unique type of nuisance faced by computer users. Rather than inflicting damage on your computer, grayware employs applications you did not intend to use that could lead to strange system behavior, such as high consumption of computing resources and unwarranted system slowdowns.
Unlike other types of malware that can cause serious harm to your system, grayware is mostly an annoyance. It can, however, lead to issues that may concern you like over-using system resources and causing your computer to lag. So, while it may not directly harm your system, it can certainly create unnecessary frustration and disrupt your usual computer use.
Given that, it's important to understand the differences between grayware attacks and other, more harmful types of system attacks. For example, while a virus might delete or corrupt files on your computer, grayware might merely slow down your system or cause it to behave oddly. Understanding these differences can help you better protect your computer and data.
And speaking of protection, having knowledge about grayware's existence and its potential signs is an important step towards your preventative measures. Recognizing unusual system slow-downs or sudden high resource usage can tip you off to potential grayware on your computer. Always stay vigilant and ensure to keep your systems protected.
Grayware refers to a somewhat ambiguous classification of software that straddles the fine line between legitimate applications and harmful viruses. Although grayware does not explicitly harm your computer, it is critical to detect and eradicate it promptly in order to prevent unexpected system behaviors or potential downtime.
From a broader perspective, grayware exists primarily due to its borderline nature. Software under the realm of grayware may not be inherently harmful, however, they often possess attributes or actions that can cause issues. They may range from undesirable to malicious, impacting a system in numerous ways beyond merely causing 'unwanted system behavior or downtime'. Understanding these nuances is critical to mitigate associated risks.
Examples of grayware often brought up are adware and spyware. To fully appreciate the potential threat of grayware, it's helpful to compare it with other types of malware such as ransomware and backdoor attacks. Such comparisons paint a clear picture of the extent of potential threats within the malware spectrum.
The consequences of grayware manifest in a number of ways, with the severity varying based on its classification and the system's vulnerability. From slower system performance to unauthorized data access, the ripple effects of grayware infiltration can have tangible impacts. Silently working in the background, grayware can collect personal information, disrupt user experience, and pose other stealthy threats.
The importance of understanding these malware attacks is matched by the need to adopt preventive measures against falling victim to grayware. There exist ways to protect your system such as keeping software regularly updated, using reputable antivirus software, and practicing caution when installing new applications or clicking on links. Equipped with these strategies, users can anticipate and ward off potential grayware threats.
22. Understanding Exploit Kits
Exploit Kits are a major cyber security concern. Let's delve deeper into what these are, how they operate and why they pose such a significant threat in the cyber world.
So, what exactly is an Exploit Kit? In simple terms, it's a type of malicious toolset used by cybercriminals to exploit security vulnerabilities in systems, leading to a variety of attacks.
The functioning of these Exploit Kits can be quite complex. These kits scout for vulnerabilities within a system and then exploit them, often to infiltrate malware. Understanding their functionality can provide a better insight into their threat level.
Exploit Kits are considered to be a serious threat because they are, unfortunately, very effective. They can cause serious damage, such as data breaches, network compromise, and even financial loss. There have been numerous cases where the use of Exploit Kits led to widespread damage, reinforcing the importance of security measures.
So, how can we protect ourselves against such threats? Good question! A combination of secure online habits, dependable antivirus software, and regular system updates can significantly reduce the risk. Including these practices in your daily routine is an effective way of creating a secure cyber environment.
Let's take a closer look at some real-life instances where Exploit Kits have wreaked havoc, to better understand their potential damage and the importance of protective measures.
Overall, the aim here is to inform and engage you about the implications of Exploit Kits and enlighten you about the precautionary steps that can be taken to ensure safer online experiences.
Exploit kits play a critical role in the toolbox of cybercriminals, enabling them to take advantage of inherent weaknesses in software systems. These flaws serve as gateways for cybercriminals to infuse various types of damaging programs into a targeted computer system. Defined as malware, these programs represent a substantial security concern.
Security vulnerabilities provide a ripe opportunity for such malicious programs to enter a system. Exploit kits, known for their unique codes, facilitate this penetration by identifying system loopholes, supplying malware attacks, and promoting system damage. The sophisticated nature of these codes makes them a preferred method for executing cyberattacks, specifically malware incursions.
One critical element of cybercrime is the speed of attack - the faster, the better. This is precisely where exploit kits come in handy. Cybercriminals often use them in what's known as 'drive-by' attacks on unsuspecting victims. These attacks are akin to a sniper's sudden assault - unknown, unexpected, and often successful. Drive-by attacks occur when a user visits or 'drives by' a malicious website, either innocently or due to a link within a phishing email. Upon loading the infected webpage, the exploit kit automatically scans the user's system for vulnerabilities and, if found, deploys its payload.
Thus, knowledge about various types of malware and the role of exploit kits in their deployment is vital in the sphere of digital safety. Instances of real-world attacks would underscore the severity of these cyber threats.
However, the story does not end with understanding the danger. Knowing how to defend against such cyber threats is just as essential, if not more so. It is pivotal to talk about the various preventive measures one can take against malware attacks and the role exploit kits can play in this defense. A well-rounded approach to security that addresses all angles of threats and defenses is our best bet against the increasing cyber threats in today's digital world.
23. Unmasking the Logic Bomb: A Hidden Threat
Imagine a hidden ticking time bomb in your computer, programmed to explode or perform an action at a certain time or under specific circumstances - that's what we call a "Logic Bomb." This malicious type of software tends to lay dormant until a specific condition is met. Similar to a real-life time-bomb, once the logical conditions or triggers are met, the so-called Logic Bomb "detonates" and carries out its destructive functions. These functions can result in severe damages, as we will discuss below.
How does a Logic Bomb infect a system? Let's draw a real-life scenario. A disgruntled employee might plant a Logic Bomb, so that it infects the system and performs its destructive action, like deleting data, after his resignation or in case of his termination. As you can see, the placing of Logic Bombs is often premeditated and can have extreme consequences.
If a Logic Bomb indeed infiltrates your system, the range of potential harm is vast. It can delete or corrupt confidential data, rendering your network inoperable, and upsetting critical functions for both individuals and businesses alike. And due to its latent nature, detecting a Logic Bomb before it “detonates” is extremely challenging.
There are some notorious cases of Logic Bomb attacks that left a mark in the world of cybersecurity. A famous one is the case of a Siemens software developer in Germany, who planted a Logic Bomb that resulted in the shutting down of many utilities and large public services. This case highlighted the imminent threat that this type of malware represents.
To reduce your chances of falling prey to a Logic Bomb, it's essential to take preventative measures. Ensure your systems and applications are regularly updated, and invest in top-notch cybersecurity solutions that detect and neutralize malicious software. Monitor your system’s performance and look for abnormalities. Unusual slowness, frequent crashes, or substantial changes in storage space could be signs of an impending Logic Bomb attack.
Therefore, understanding not only the basic function of this malware but also the effects of its attack on your system is crucial. It might translate into tangible costs such as data recovery expenses, lost revenue due to downtime, or even intangible costs like the loss of customer trust and reputation damage. By far, a proactive approach to cybersecurity is your best line of defense against threats like a Logic Bomb.

Commonly referred to as slag code, a logic bomb is a subset of malware that's embedded into a software program. This sinister code waits, invisible to the end-user, until a specific condition is met, be this a particular date, time, or logical event. Once triggered, the consequences can range from mild, such as a harmless prank, to severe including entire system crashes or the theft of sensitive data. As such, understanding the potential threats posed by a logic bomb, along with defensive measures such as regular system checks and up-to-date antivirus software, is essential in the broader context of preventing malware attacks. This connection between understanding logic bombs and malware prevention, as outlined in the summary of this article, helps shed more light on the importance of cybersecurity for our systems.
A logic bomb, a type of malware, plays a significant role in supply-chain attacks. The software is designed to 'detonate' or execute harmful actions only when certain preset conditions are fulfilled, making it insidious and potent. Detailed explanation regarding the workings of a logic bomb, and their typical activation triggers, would further our understanding of this form of malware.
It's important to shed light on the statement, "it is undetectable until it's too late to halt the attack". Highlighting why it remains hidden until such a point and giving examples from real-life encounters where efforts to stop the attack were futile would allow the audience to grasp the practical implications of logic bombs. Knowledge about the workings of these kinds of malware attacks can significantly aid in thwarting major cyber threats.
The severity of the damage that a logic bomb can potentially inflict needs to be emphasized, given the article's focus on the disastrous outcomes of malware attacks. Distinguishing how different a logic bomb is from other malware mentioned in the summary will further enrich the content and make it more comprehensive.
The paragraph ought to conclude with a potent statement underscoring the gravity of malware attacks, particularly those involving logic bombs. It should also stress the importance of proactive measures to prevent such threats. This vital understanding and awareness are the first steps towards a safer cyber world.
Logic bombs, a type of malicious code, can cause a range of damage. The severity of this damage can vary greatly, as attackers have an unlimited array of conditions from which they can append this malicious code. When a logic bomb is triggered, it can lead to diverse impacts. These can include actions such as 'hard-drive cleaning' (which essentially means wiping clean all data stored on a computer's primary storage system), deletion of various files, and corruption of sensitive data (which means altering or degrading valuable information so that it becomes unreadable or unusable).
Considering the damage that logic bombs can do, it's important to understand the preventive measures that can be taken against them and how these preventative steps compare with those used against other types of malware. By understanding these comparisons, readers can better understand the unique threats posed by logic bombs.
On a practical level, adding real-world incidents where logic bombs have caused significant issues can help provide a clearer understanding for readers. For instance, the fact that logic bombs have been used in cyber-terrorism to disrupt or completely shut down vital infrastructure highlights the very real threat they pose.
To round out this discussion, it would be beneficial to compare the impacts of logic bombs with other types of malware. Doing so can help readers differentiate between them and understand how their own systems might be uniquely affected by each type. For instance, while logic bombs can wipe an entire hard-drive clean, other types of malware might simply hijack a computer's processing power for nefarious purposes.
Understanding Droppers: A Type of Malware Attack
Let's delve into the concept of "Droppers," a significant type of malware attack. It is essential to understand what they are and how they function. These types of malware, as their name suggests, act as 'drops' in a computing system to infiltrate it and cause damage.
A thorough understanding of their operation is crucial in understanding their potential impact. Equipped with this knowledge, we can begin to comprehend the significant damages they can inflict on a system.
We should also take a look at some practical, real-world examples of such attacks. These case studies will further enlighten us about the imminent threat these attacks pose and why we should learn to prevent them.
Another critical aspect to address is the infiltration methods of these malware 'Droppers.' Awareness about these methods can lead us to effective preventative measures against such attacks on our computing systems.
We cannot forget the aftermath of a successful Droppers attack. Highlighting the potential consequences can serve as a wake-up call about its severity and the importance of adequate prevention measures. This issue becomes even more significant when a Dropper attack is compared to other varieties of malware attacks.
By discussing the severity of Droppers in comparison with other forms of malware, we can help readers prioritize their cybersecurity efforts appropriately. A thorough understanding of Droppers can enhance our overall knowledge of malware threats and help us navigate the digital world more securely.
In the complex world of cybersecurity, "droppers" play a key role. For those unfamiliar with the term, a dropper is a type of computer program leveraged by hackers to infiltrate systems surreptitiously. These are unique because unlike conventional, detectable malware, droppers typically do not contain malicious code, making them virtually invisible to antivirus software.
To help you better understand, let's take an example from the past. Remember the major data breach that took place a few years ago? The one that compromised millions of accounts worldwide? In that incident, the hackers were said to have used a dropper to introduce a malicious program into the targeted systems.
Once deployed, a dropper can do a lot more than just sneakily install malicious applications. It has the potential to download new malware or even carry out updates for a malware already installed in a system. Now, you may be wondering what all this means for an everyday computer user like you. Well, in simple terms, a dropper can lead to a variety of undesirable consequences, from data theft to a severely damaged computer system.
So, how can we guard ourselves against the potential threat posed by droppers? It begins with informed vigilance. Always be cautious when downloading files from the internet, especially if they are from unknown sources. Regularly update your computer's antivirus software. Be sure not to overlook system updates as these often include patches for security loopholes that hackers could otherwise exploit.
Finally, let's revisit the broader topic of our discussion: malware. While droppers and viruses both fall under this category, they serve different purposes in a hacker's arsenal. Remember, a virus is just one form of damaging software, while droppers act as vehicles for delivering these harmful programs. They all add up to the diverse landscape of cyber threats we face today.
25. Exploring Polymorphic Engines: An In-Depth Analysis
In this segment, "25. Exploring Polymorphic Engines: An In-Depth Analysis", we'll dig deep into the details of what Polymorphic Engines are, particularly their involvement in malware attacks. We're first going to note their purpose and their execution path, and then go one step further to decipher the serious risk these engines pose. We'll also highlight what sets Polymorphic Engines apart from other kinds of malware we've discussed in this article.
For a more comprehensive understanding, we'll take a look at some specific instances where Polymorphic Engines were utilized in genuine cyber-attacks. These real-world examples will add a layer of relatability to our discussion, helping you to better understand the threat of these engines.
And, as with all other sections of our article, we won't just stop at understanding these risks. In keeping with the core theme of our discourse, we dive into practical approaches on how to avoid falling victim to Polymorphic Engine attacks, equipping you with the necessary tools to protect against such threats.
A polymorphic engine, more commonly known as a mutating engine, is an ingenious piece of software designed to transform an application's code. Still keeping its functionality the same, these disguised versions render the application unrecognizable to some anti-virus tools. One way hackers utilize mutating engines is in obfuscating malware attacks, particularly viruses and shellcodes. This camouflage makes it difficult for anti-virus and antimalware software to detect and neutralize them.
Before diving in further, let's pause and understand a few key terms. In the realm of cybersecurity, malware encompasses any software programmed to cause harm or gain unauthorized access to computer systems; a virus, on the other hand, is a specific type of malware known for its ability to duplicate and distribute itself through your files and documents. So, every virus is malware, but not every malware is a virus.
Please note, malware doesn't just end at the virus. There exists an array of other malicious attack techniques, such as ransomware, adware, malvertising, and backdoor breaches. Each of these follows a unique pattern of intrusion and damage, making it crucial for anti-malware tools to be well-equipped and up-to-date to prevent them effectively.
To provide a clearer picture, imagine trying to prevent ransomware, a type of malware that blocks user access to a system or personal files and demands a ransom to release it. Awareness of this will guide in taking measures like keeping regular backups, using robust antimalware suites, and being cautious of phishing emails.
Speaking of preventive measures, let's underline their importance in dealing with the daunting impacts of these cyber-attacks—understanding how antimalware and antivirus scanners work is the first step in this direction. These forms of defense software are configured to scan your computer continually for any malicious program. Once a threat is detected, it is either quarantined or deleted to stop its malicious activity.
Finally, for those who are not tech-savvy, here's a list of simple steps you can implement to protect yourself from cyberattacks:
26. Scareware
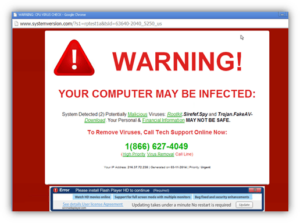
Scareware malware is a type of malware that manipulates users. It tricks users into downloading or purchasing unwanted harmful programs out of anxiety, perception of possible threats, or shock.
Malicious programs such as malware, form a category within which exists other detrimental applications. This includes the likes of ransomware, deceptive security programs, and fraudulent software.
Sneaky yet harmful, these threats often use scare tactics, convincing the unsuspecting individuals that an imminent harm will soon befall if they don't employ these programs. The irony lies in the fact that, more often than not, this so-called protective software evolves into another form of the malware.
Unfortunately, each of these threats - ransomware, rogue security applications, and scam software - are interconnected, all existing under the umbrella of malware waiting to exploit any vulnerability. They can each lead to serious repercussions, such as data loss, financial harm, and a breach of personal privacy. Do not let their differences fool you, they are unified in their objective to cause damage.
The extent of damage caused by malware attacks is truly shocking. Imagine a world where 40% of all small and medium-sized businesses have fallen victim to malware! When faced with such frightening figures, being informed and staying vigilant is a necessity.
As a reader, your best weapon against these threats is awareness. Beware of software that promises miracle solutions or features that seem too good to be real - these could potentially be malware in disguise. Stand guard and stay informed.
